Synthesis of Water-Soluble Polyethylene Glycol Fumarates for Biomedical Applications
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31489/2959-0663/2-24-7Keywords:
polyethylene glycol, polyethylene glycol fumarate, fumaric acid, polyester resin, macromonomer, hydrogels, FTIR- spectroscopy, 1H NMR-spectroscopyAbstract
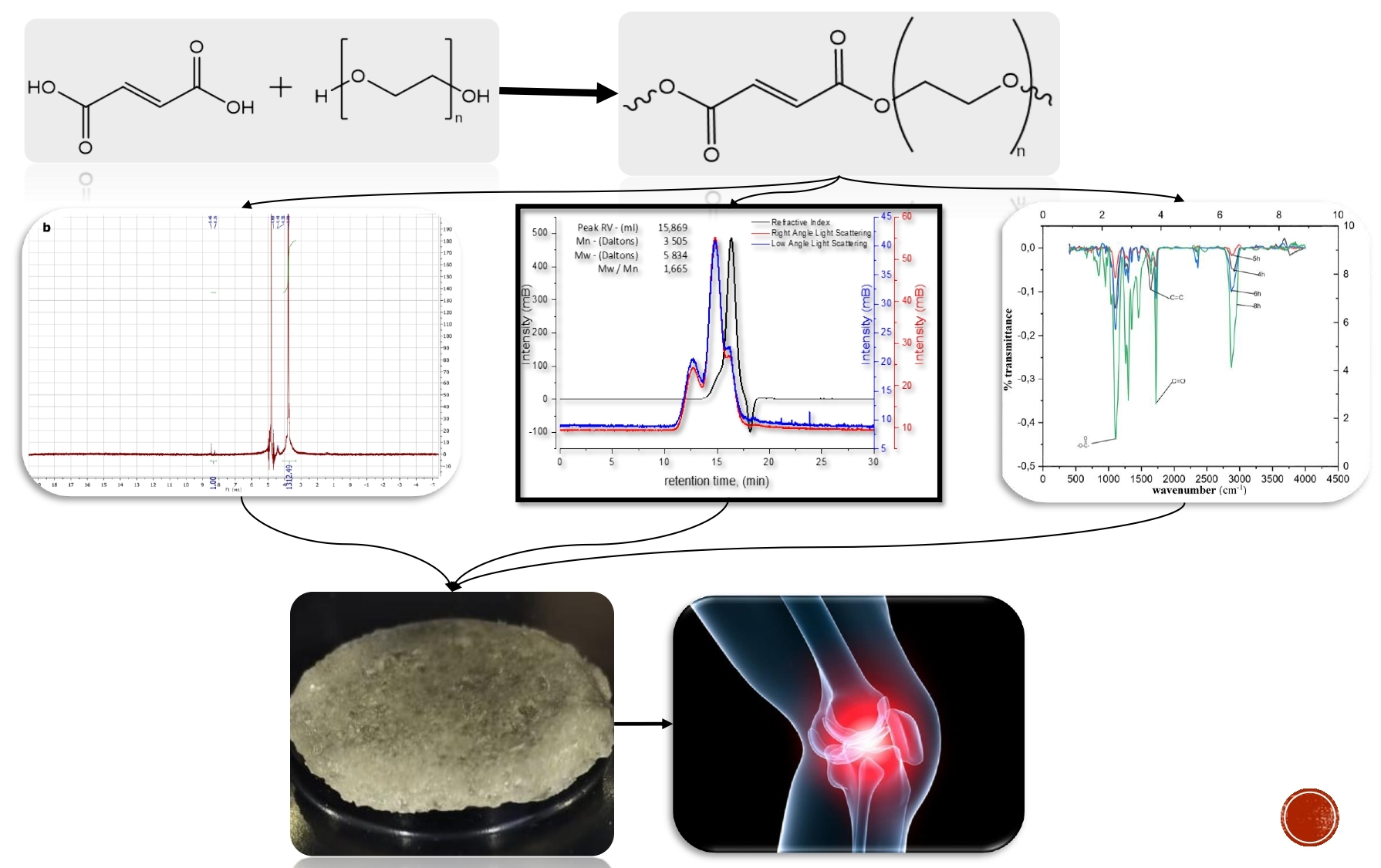
Polyethylene glycol fumarate (PEGF) with controlled structural composition has been obtained for further synthesis of double network crosslinked hydrogels for biomedical applications. The copolymer has been synthesized by polycondensation reaction of fumaric acid and polyethylene glycol (PEG-600). Molecular weight of PEGF has been determined by gel permeation chromatography to be approximately 6000 Da with gel permeation chromatography. The polycondensation of fumaric acid and PEG-600 was studied throughout the reaction process. The structure of the reaction product has been evidenced using FTIR- and 1H NMR-spectroscopy. The quantitative ratios of the amount of –C=C– bonds and –COO groups to –C=O groups in the obtained PEGF have been estimated from IR-spectra for different synthesis time. The time-dependence of molar ratio of double bonds to methyl groups in PEGF has been obtained from corresponding 1H NMR-spectra. FTIR and 1H NMR-spectroscopy, both, demonstrate that after the end of reaction the unsaturated –C=C– double bonds remain in the structure of the macromonomer, that is essential for further preparation of cross-linked hydrogels. The addition of the tightly cross-linked network of polyvinyl alcohol leads to formation of highly tough biocompatible material for preparation of the artificial meniscus which can further be used as a solution n the treatment of diseases such as osteoarthritis.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Yerkeblan M. Tazhbayev, Akerke T. Kazhmuratova, Lyazzat Zh. Zhaparova, Ulugbek B. Tuleuov, Yermauyt Nassikhatuly, Elizaveta S. Mitricheva, Alexander L. Kwiatkowski, Andrey V. Shibaev

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.



