A New Method for the Synthesis of Ald(ket)azines and their Antioxidant Activity
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31489/2959-0663/4-24-7Keywords:
aldazines, ketazines, azines, synthesis, Schiff bases, hydrazinium monoacetate, condensation reactionAbstract
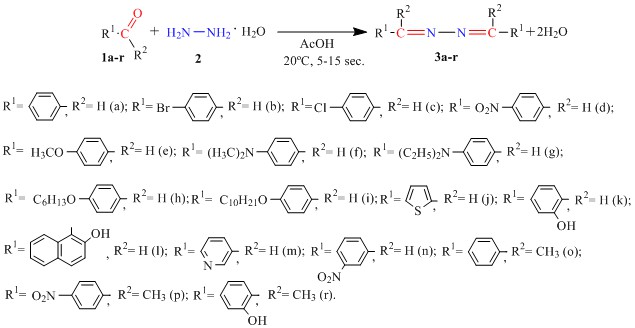
The synthesis of biologically active compounds frequently requires the establishment of specific conditions (such as pressure, temperature, medium, solvent, and catalyst) or the use of expensive equipment. An important task is the search for simple synthesis methods for promising biologically active compounds. This paper presents data on a rapid method for the synthesis of ald(ket)azines (azines) with a variety of biological and physicochemical properties. Hydrazine hydrate reacts readily by condensation with aromatic (heterocyclic) aldehydes or ketones to form azines. The reaction occurs at room temperature in acetic acid. The synthesis is completed in a short period of time, between 5 and 15 seconds, with yields of 32 % to 98 % after recrystallization. The formation rate of ald(ket)azines depends on the reaction medium and the presence of hydrogen donors in the system, and increases with increasing acidity. The investigation did not yield any discernible pattern in the impact of electron-donor or electron-acceptor substituents in the para-, meta-, or ortho-positions at aromatic (heterocyclic) aldehydes or ketones on the azines yield. The synthesized compounds were studied using 1H NMR spectroscopy, chromato-spectrometry, and elemental analysis. The Ferric Reducing Antioxidant Power (FRAP) spectrophotometric method was used to study the antioxidant activity of the compounds obtained. Compounds with an N,N-dimethyl- or N,N-diethyl group in the para-position of the aldehyde fragment of azine showed a significant antioxidant effect. The results obtained exceed the antioxidant value of ascorbic acid — an industrially used oxidation inhibitor.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Valeriy Yu. Gorokhov, Svetlana A. Zabolotnykh, Larisa G. Chekanova, Vera N. Vaulina

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.



