Sol-gel Synthesized ZnO–SrMn2O4 Nanocomposite and Its Antibacterial Properties
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31489/2959-0663/4-24-12Keywords:
Nanocomposite, antibacterial activity, spinel, zinc oxide, Sol-gel, SEM, XRD, binary oxideAbstract
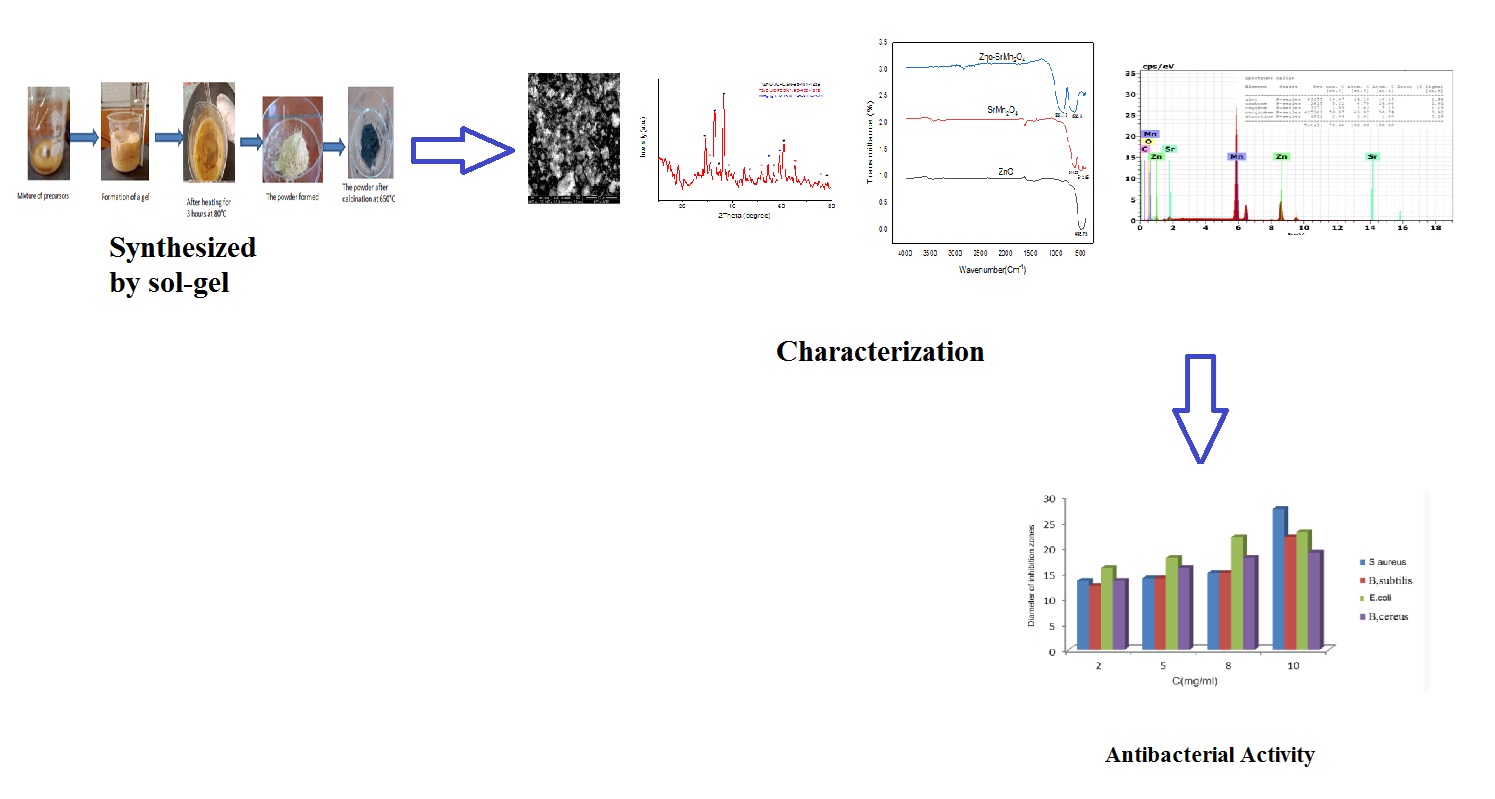
This paper presents the synthesis of new binary oxide nanoparticles (NPs), ZnO–SrMn2O4, with a spinel structure. The sol-gel technique was used to synthesize ZnO–SrMn2O4 spinel-type oxides, which were subsequently investigated for their antibacterial properties. The NPs were characterized by a range of methods, namely Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and energy dispersive X-ray analysis (EDX). The FTIR analysis revealed the presence of peaks characteristic of SrMn₂O₄ and ZnO/SrMn₂O₄. These peaks confirm the presence of metal-oxygen bonds, namely Zn–O, Mn–O, and Sr–O. SEM was used to analyze the morphology, chemical composition, and size of the nanocrystals. The morphology of the particles is observed to be more irregular in shape, with a wide range of nanoparticle sizes, from 54 to 250 nm. The synthesized nanoparticles, ZnO–SrMn2O4, were used to assess their antibacterial properties against Bacillus cereus, Bacillus subtilis, Staphylococcus aureus, as well as Escherichia coli and demonstrated pronounced antibacterial efficacy. The highest antibacterial activity was recorded against Escherichia Coli, with a diameter range of 16–23 mm, followed by the strain Staphylococcus aureus with a diameter range of 13.5–27.5 mm. The next most active strain was Bacillus subtilis, with a diameter range of 12.5–22 mm, and Bacillus cerus, with a diameter range of 13.5–19 mm. Further use of the obtained ZnO–SrMn2O4 powder is recommended for application in photocatalysis of dye degradation.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Saida Soualmi, Meriem Henni, Leila Djahnit, Hanane Hamdani

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.



