Neuroprotective, Anticancer and Antimicrobial Activities of Azo-Schiff Base Ligand and Its Metal Complexes
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31489/2959-0663/1-25-8Keywords:
azo-Schiff base ligand, coordination compounds, metal complexes, azomethine, biological activity, neuroprotective, anticancer, antimicrobialAbstract
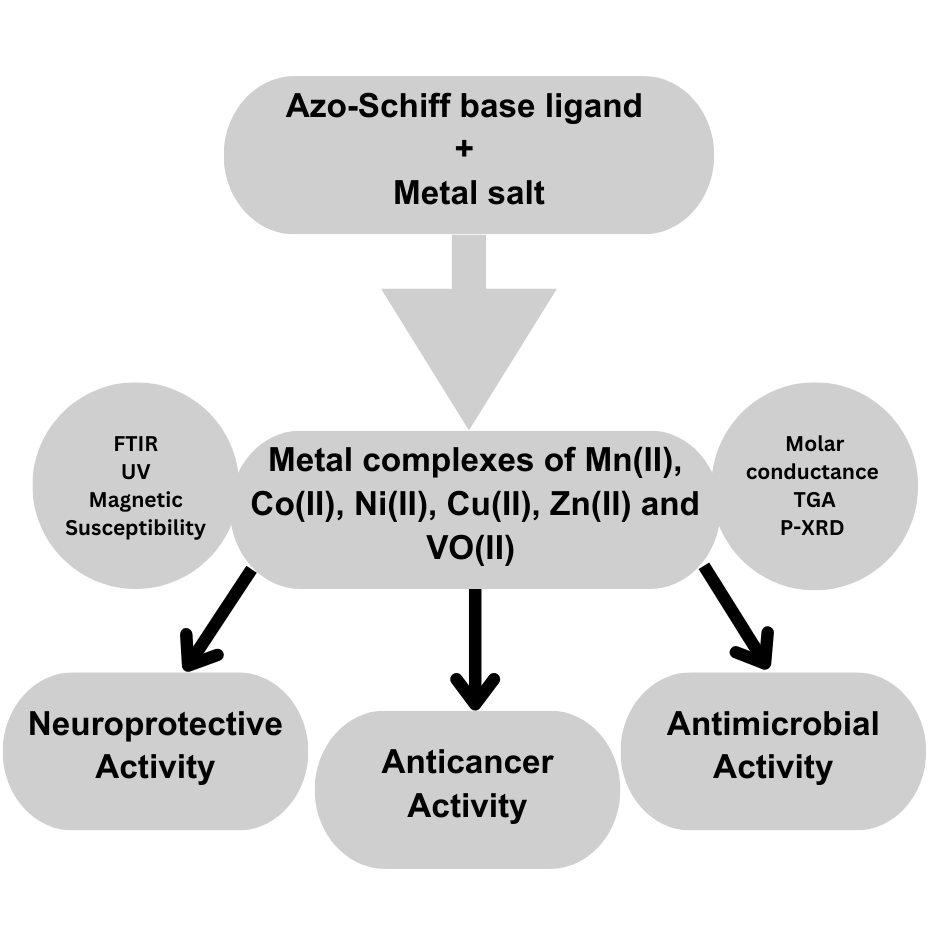
The synthesis of metal complexes of Mn(II), Co(II), Ni(II), Cu(II) Zn(II) and VO(II) from azo-Schiff base ligand was carried out by the condensation reaction of (E)-5-chloro-2-hydroxy-3-((3-nitrophenyl)diazenyl) benzaldehyde and 2-amino-4-nitrophenol. The structure of the synthesized azo-Schiff base ligand was confirmed by 1H-NMR spectra, mass spectra, FT-IR spectra. After confirmation of the azo-Schiff base ligand, metal complexes of Mn(II), Co(II), Ni(II), Cu(II), Zn(II) and VO(II) were synthesized using metal salts. These synthesized metal complexes were characterized by FT-IR spectra, elemental analysis, electronic spectra, thermal analysis, X-ray powder diffraction, molar conductivity etc. In biological studies, the neuroprotective and anticancer activities of azo-Schiff base ligand and metal complexes were investigated by methylthiazole tetrazolium (MTT) assay on SHSY-5Y Neuroblastoma Cell line and MCF-7 human breast cancer cell line using Tacrine (TAC) and 5-Flourouracil (5-FU) as reference standard drugs, respectively. Also, antimicrobial potential was screened against two gram-positive (Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus subtilis), two gram-negative (Klebsiella pneumonia and Pseudomonas aeruginosa) bacteria and three fungi (Penicillium chrysogenum, Tricoderma viride, and Aspergillus niger). Based on all the data obtained, it was concluded that metal complexes exhibit higher biological activity than ligands based on the azo-Schiff base.
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Kirti N. Sarwade, Kuldeep B. Sakhare, Mahadeo A. Sakhare, Shailendrasingh V. Thakur

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.



