Synthesis, Docking Study and Biological Evaluation of Naproxen-Based Heterocyclic Derivatives
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31489/2959-0663/1-25-3Keywords:
Naproxen derivatives, heterocyclic compounds, COX-2 inhibition, MTT assay, antibacterial, anticancer, breast cancer , anti-inflammatory propertiesAbstract
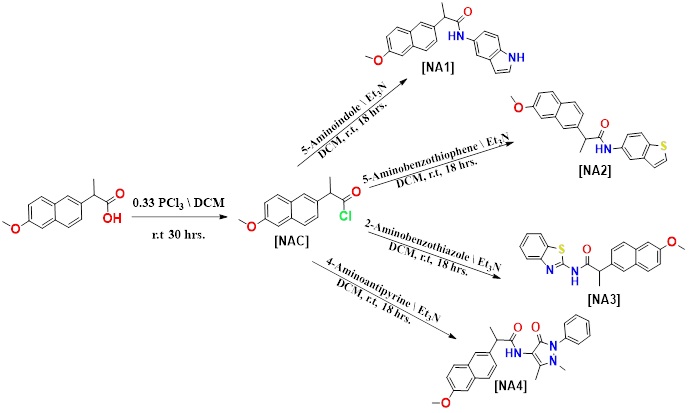
A series of Naproxen-based heterocyclic derivatives (NA1-NA4) were designed, synthesized, and evaluated for their antibacterial and anticancer activities. These heterocyclic derivatives were developed by integrating Naproxen with various heterocycles, including indole, benzothiophene, benzothiazole, and pyrazole, in order to enhance efficacy while reducing gastrointestinal side effects. The synthesized compounds were characterized using FT-IR, 1H NMR, and 13C NMR spectroscopy. The antibacterial activity was evaluated against S. aureus (Gram-positive) and two Gram-negative bacteria (P. aeruginosa and K. pneumonia) by measuring the diameter of the zone of inhibition. Compounds NA2 and NA3 showed promising inhibitory activity against the tested bacteria compared to amoxicillin. The anticancer activity of NA1-NA4 compounds against the MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cell line was assessed by determining the IC50 values (the concentration required to inhibit 50 % of cell viability). NA1 and NA3 exhibited notable antiproliferative effects with IC50 values of 11.81 and 11.08 μg/mL, respectively. Molecular docking studies of compounds NA1-NA4 were performed against COX-2 enzyme (PDB Code: 3NT1) using MOE software. The compounds showed strong binding affinities, indicating potential anti-inflammatory properties. Collectively, the antibacterial, anticancer, and molecular docking data suggest that these Naproxen derivatives possess promising multifunctional therapeutic potential.
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Ammar A. Awad, Mohammed N. Maged, Dhulfiqar A. Abed, Osamah N. Wennas, Noor Z. Kbah, Ayad A. Disher

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.



