A Novel Mannich Based Metal II Complexes: Synthesis and Characterization of Magnetic, Conductivity and Antimicrobial Properties
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31489/2959-0663/1-25-5Keywords:
Antimicrobial Activity, Ciprofloxacin, Clotrimazole, Docking, Grindstone, Mannich base, Metal Complexes, XantheneAbstract
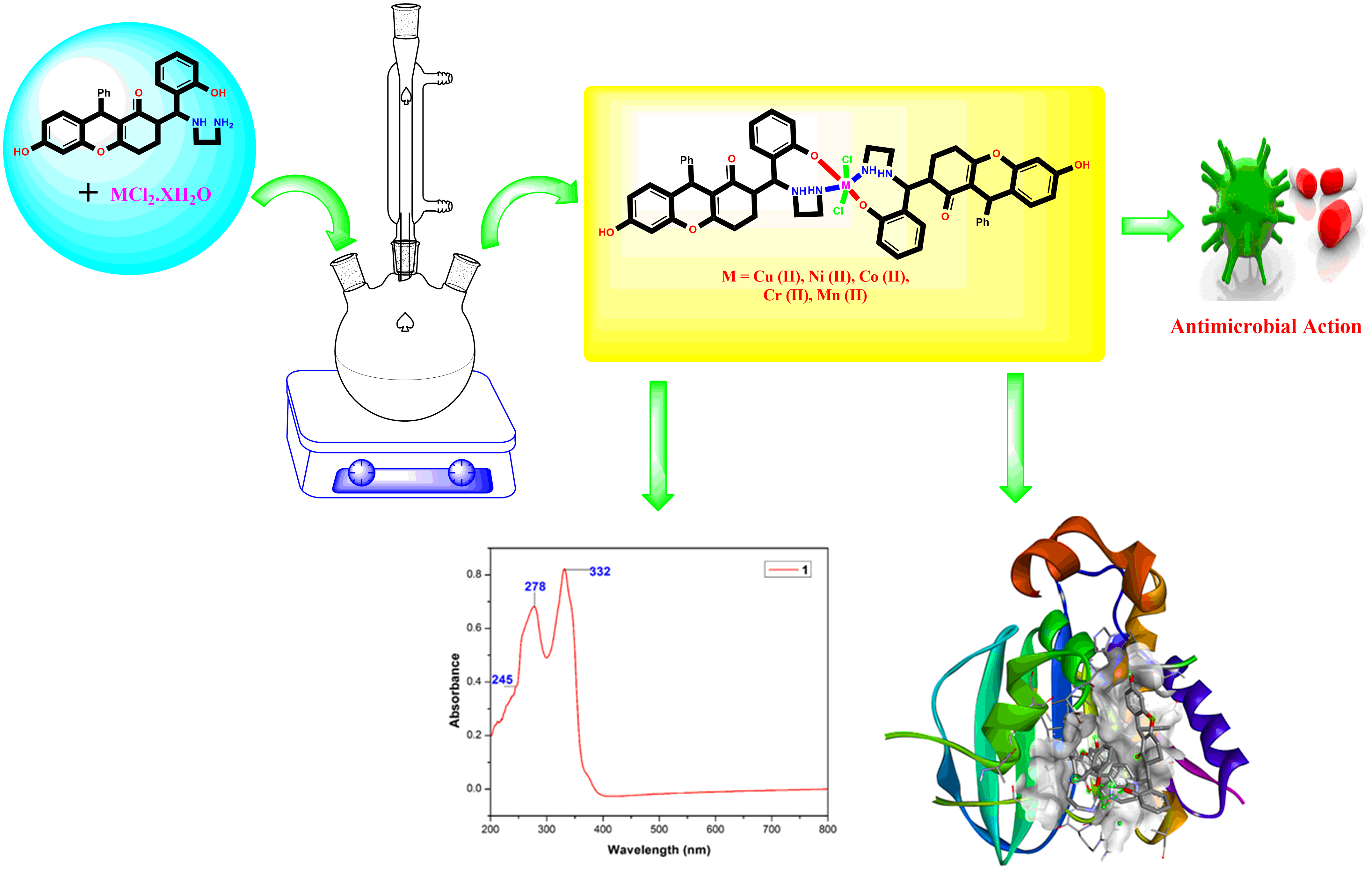
A novel Mannich base (2R,9R)-2-((S)-((2-aminoethyl)amino)(2-hydroxyphenyl)methyl)-6-hydroxy-9-phenyl-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-xanthen-1-one (LI), composed from xanthene, salicylaldehyde, and ethylenediamine, was employed to synthesize unique complexes of Ni(II), Mn(II), Cr(II), Co(II), and Cu(II). The structural characteristics of the complexes were determined by studying microanalytical findings and using analytical methods such as EPR, FT-IR, 1H & 13C NMR, and UV-visible spectroscopy. The electronic spectra of the complexes suggested that the metal ion is fenced with octahedral structure. The molar conductivity of the metal chelates in DMSO was shown in the range of 18–28 Ω–1mol–1cm2. The EPR studies of the copper complex dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) was obtained at temperature of 300 K, and its unique characteristics were analysed. The antimicrobial potential of the ligand and its complexes has been thoroughly examined towards K. pneumaniae, S. aureus, P. aeruginosa, E. coli, C. albicans, C. neoformans, M. audouinii, A. niger microorganisms. Experimental results have demonstrated that all of the complexes exhibit substantial antimicrobial action when related to both the unbound ligand and the standard. Furthermore, the validity of the biological research was verified through molecular docking antifungal and antibacterial tests. Overall, the obtained results confirm the multidirectional antimicrobial efficacy of the new Mannich base complexes and demonstrate their high pharmaceutical potential for further studies.
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Manimagalai Ramasamy, Gurunathan Velayutham, Pitchaipillai Ramar

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.



