H2S Properties and Temperature Effects on the Response of Pristine and Al-Doped ZnO Gas Sensor
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31489/2959-0663/1-25-10Keywords:
Al doping, ZnO cluster, pristine, H2S gas sensor, DFT, transition state, autoignition temperature, activation energyAbstract
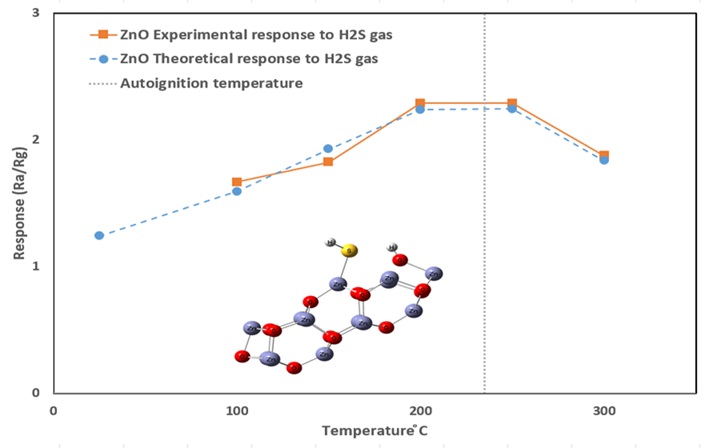
H2S is a poisonous gas that needs to be censored to protect humans from its exposure. H2S gas sensitivity and interaction with pristine and Al-doped ZnO clusters were studied using the transition state theory method. The reaction of ZnO with H2S gas is usually weak and can be enhanced by doping. Elements or their oxides, such as platinum group elements, are traditionally used as doping substances. However, the use of other cheaper elements or oxides such as Al or Mn also increases the reaction rate. The mechanism of increasing the reaction rate and sensitivity by Al doping is the subject of present work. The calculation results show that Al-doped ZnO increases the sensitivity towards H2S by growing the resistance of Al-doped ZnO due to lattice distortion. The Gibbs activation energy remains almost the same as calculated by the present model. In conclusion, it should be noted that good agreement between theory and experiment was achieved in terms of temperature-dependent reaction rate, gas response, recovery and response time for different doping ratios. For the first time, the autoignition reaction and temperature of H2S were considered in sensors. Further improvement in transition state theory is needed to include further gas sensor features.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Mudar A. Abdulsattar, Sawsan M. Almaroof

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.



