Study of the Effect of Potassium Chloride on the Coagulation of PTFE Dispersion by Optical Methods
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31489/2959-0663/1-25-11Keywords:
PTFE, dispersion, surfactant stabilization, coagulation, aggregate stability, optical density, spectrophotometry, dynamic light scatteringAbstract
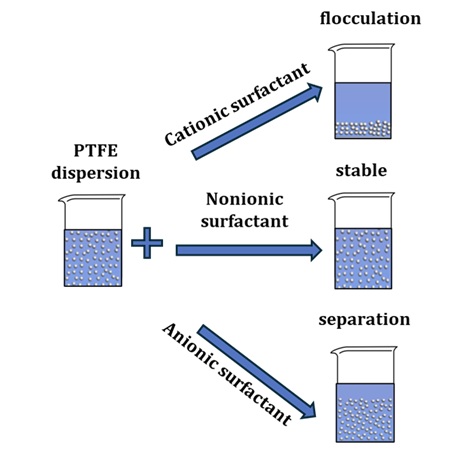
Electrolyte stability of fluoroplastic-4D dispersion was investigated by optical methods. Potassium chloride (KCl) solutions of various concentrations were used as electrolytes causing coagulation. The kinetic dependences of the influence of KCl concentration on the optical density of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) dispersion were obtained. The maximum in the time dependences of optical density is associated with the particle aggregation processes and the subsequent loss of sedimentation stability of the system. With increasing KCl concentration, this dependence changes: induction period decreases and the peak of the curve narrows. The change in the shape of the kinetic curves with an increase in the electrolyte concentration is associated with the processes of particle dehydration of dispersed phase, desorption of the stabilizer into the solution and the transition of the system from an adsorption-saturated to an adsorption-unsaturated state. The results of measuring the coagulate size of the PTFE dispersion with 2.5 M KCl in different sections of the kinetic curve by the dynamic light scattering (DLS) method correlate with the results of optical density measurements. The data obtained confirm the multi-stage coagulation process, in which the stages of latent coagulation, aggregation, inhibition of coagulation, and loss of sedimentation stability of the system can be distinguished.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Marina G. Shcherban', Ekaterina A. Ivanchina, Ilya V. Sedusov, Valeriya V. Sosunova, Konstantin P. Novosyolov

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.



