Gel-Phase Synthesis and pH-Sensitive Swelling-Structure Relationships of N-Carboxyethylchitosan
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31489/2959-0663/2-25-6Keywords:
Carboxyethylchitosan, biopolymer, gel phase synthesis, derivatization, Michael reaction, pH-sensitive swelling, porosity, green chemistryAbstract
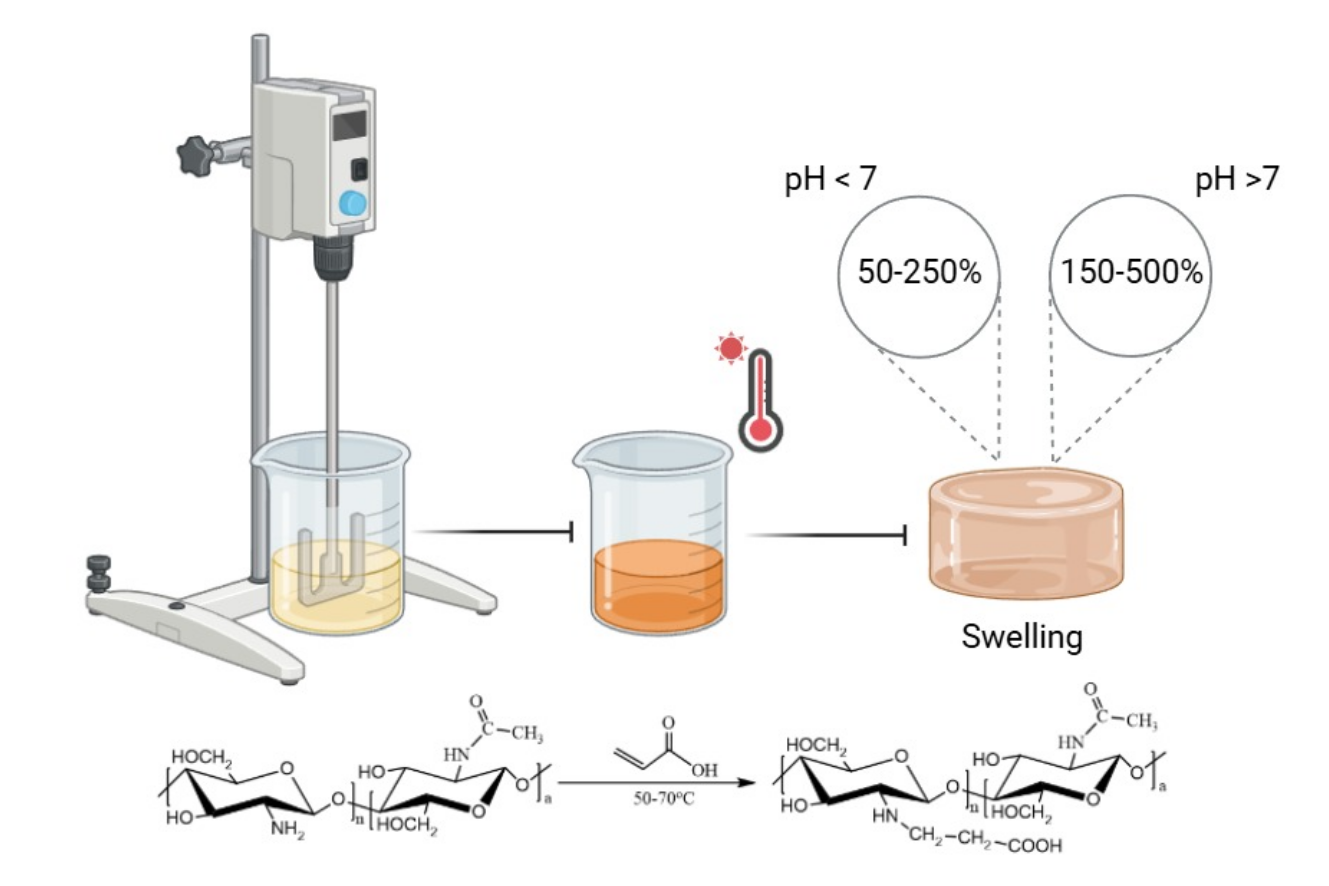
The applicability of native chitosan-based compositions is constrained by their limited solubility in weakly alkaline and neutral media, a consequence of inherent structural features. To overcome this limitation, carboxyalkylation strategies such as the gel-phase Michael synthesis of N-carboxyethylchitosan (N-CEC) were investigated with a focus on optimizing reaction parameters to enhance yield and tailor biopolymer properties. Structural confirmation of the synthesized polymers was performed via FT-IR and SEM, while elemental analysis quantified the degree of substitution (DS), which correlated with temperature in the following way: DS = 0.96–1.10 at 50 °C, 1.07–1.12 at 60 °C and 1.16–1.32 at 70 °C. Porosity measurements indicated pore sizes ranging from 50 to 200 µm in all samples; however, total porosity varied significantly, reaching a maximum of 15 % at 70 °C and decreasing to 4–10 % at lower temperatures. N-CEC exhibited pH‑dependent swelling, with minimal expansion (100–150 %) at low pH and a 2–3-fold increase at pH > 7, which was attributed to COO⁻ group formation. These findings position N-CEC as a promising material for pH-responsive applications.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Polina I. Dubovskaia, Arsalan Saeidi, Anna A. Pronchenko, Anastasiia I. Drannikova, Ivan A. Lukoyanov, Farida K. Aripova, Mariia E. Savenko, Elizaveta A. Veretennikova, Alexander V. Pestov, Ekaterina A. Litvinova, Aleksandr A. Drannikov

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.



