Polylactide Acid-Based Nanoparticles for Controlled Delivery of Isoniazid and Rifampicin: Synthesis, Characterization, and In Vitro Release Study
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31489/2959-0663/2-25-12Keywords:
drug delivery systems, nanoparticles, polylactic acid, anti-tuberculosis drugs, double emulsion, flow cell method, vertical diffusion method, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, ultrasonic homogenizationAbstract
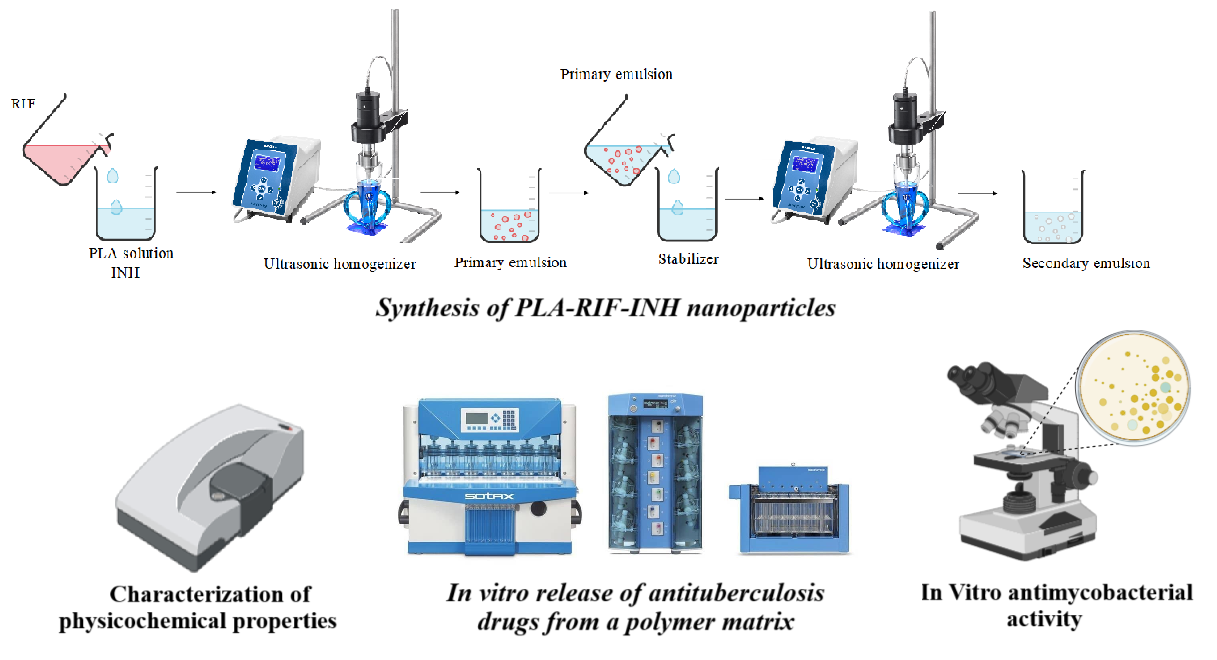
The global problem of tuberculosis (ТВ) requires advanced drug delivery systems that improve treatment efficacy. In this study, polylactic acid (PLA)-based drug carriers were developed for the controlled delivery of the first-line anti-TB drugs isoniazid (INH) and rifampicin (RIF). The main objective of this study is to improve PLA-based NP formulations through optimization to achieve maximum drug content coupled with enhanced stability to improve treatment outcomes. PLA-RIF-INH nanoparticles (NPs) were prepared by double emulsion method using ultrasonic homogenizer, using different surfactants (polyvinyl alcohol, Tween-80 and Pluronic F-127) and with different organic solutions (dichloromethane, dimethyl sulfoxide and ethyl acetate) at different phase ratios. The produced NPs had an average size of 197±8 nm with a polydispersity index of 0.287±0.048 and contained 23±2 % INH and 20±8 % RIF for a NPs yield of 65±2 %. The release of drugs from PLA NPs was investigated using the flow cell method and the vertical diffusion method at different pH values simulating gastrointestinal conditions. It was shown that PLA-RIF-INH NPs have pronounced antimycobacterial activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv and isoniazid-resistant strain, which confirms the prospect of their use in tuberculosis therapy.
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Aldana R. Galiyeva, Nazgul A. Yessentayeva, Dias T. Marsel , Arailym T. Daribay, Daniyar T. Sadyrbekov , Rouslan I. Moustafine, Tatyana V. Kutulutskaya

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.



