A Mini Review on Track-Etched Membranes Potential for Sensors Development
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31489/2959-0663/3-25-12Keywords:
biosensors, functional nanomaterials, stimuli-responsive materials, track-etched membranes , biosensors, composite track-etched membranes , hybrid membranesAbstract
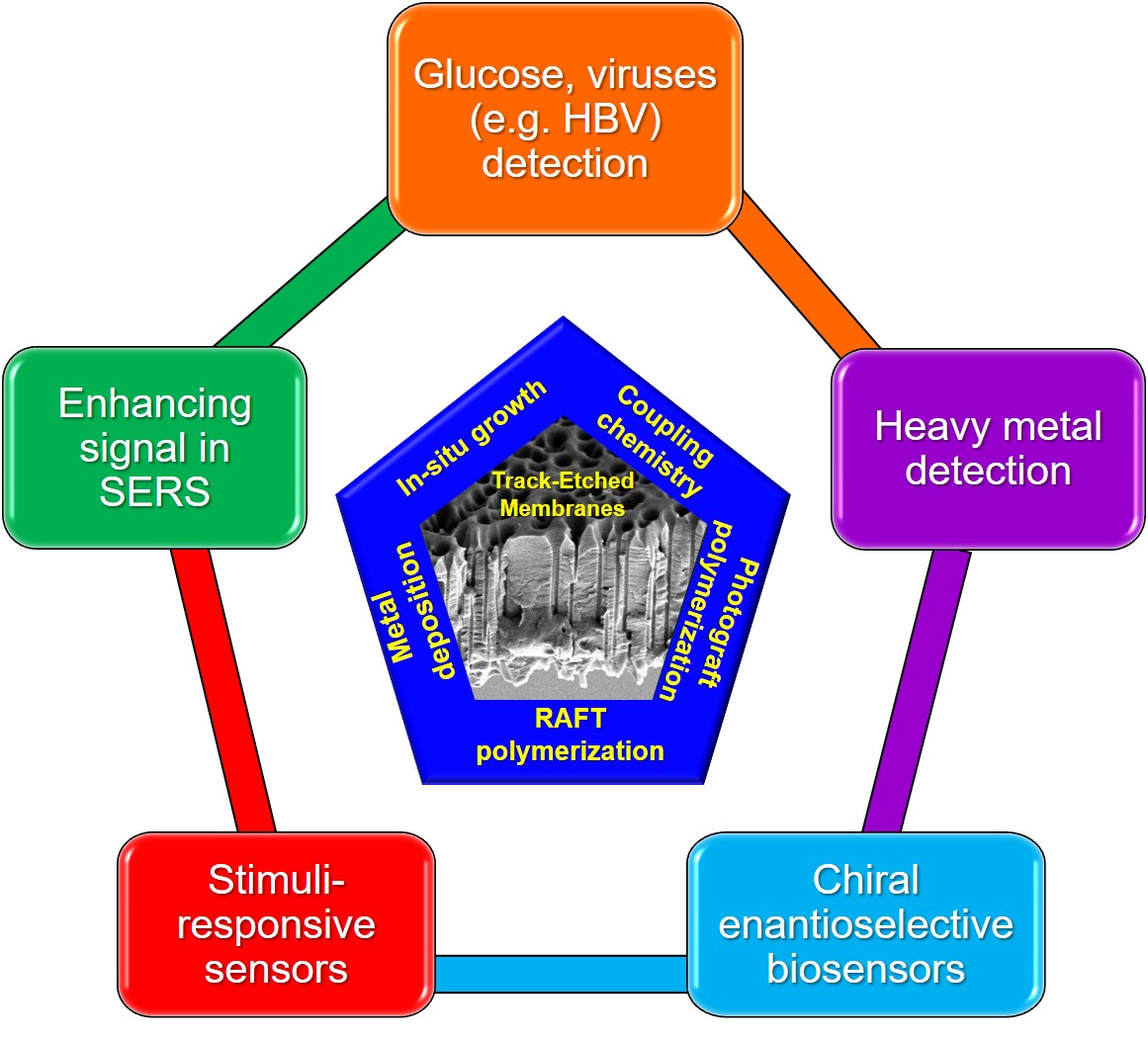
Track-etched membranes (TeMs) have emerged as a promising class of nanostructured materials for the development of advanced sensing platforms. Owing to their highly uniform pore architecture, controllable dimensions, and versatile surface chemistry, TeMs can be used to create highly sensitive, selective, and robust sensors. This review provides a comprehensive overview of recent advances in the use of TeMs for sensor development, with a particular emphasis on functionalization strategies and application domains. The review discusses stimuli-responsive TeMs in detail which are capable of dynamic switching in response to environmental triggers such as pH, temperature, light, or redox. Functional nanochannels engineered through various modifications, such as polymer grafting or metal-organic frameworks incorporation, exhibit unique ionic transport behaviors suitable for real-time detection and biomimetic sensing. TeMs have also shown considerable potential in the detection of toxic metal ions, where tailored chemical groups and hybrid interfaces enable sub-ppb sensitivity in complex matrices. Furthermore, their capacity to host biomolecules like DNA probes, antibodies, or enzymes opens avenues for biosensing applications, including clinical diagnostics, virus detection, and neurotransmitter detecting. Additionally, their integration into wearable devices highlights their potential for flexible, real-time health monitoring. Challenges related to large-scale manufacturing, long-term stability, and standardization remain and are addressed in this review. Looking forward, TeMs have potential to bridge the gap between lab-scale innovation and practical sensor technologies, offering solutions for environmental, biomedical, and industrial applications.
References
Brighenti, R., Li, Y., & Vernerey, F. J. (2020). Smart Polymers for Advanced Applications: A Mechanical Perspective Re-view. Frontiers in Materials, 7, 548239. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmats.2020.00196 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fmats.2020.00196
Dayyoub, T., Maksimkin, A. V., Filippova, O. V., Tcherdyntsev, V. V., & Telyshev, D. V. (2022). Shape Memory Polymers as Smart Materials: A Review. Polymers 2022, Vol. 14, Page 3511, 14(17), 3511. https://doi.org/10.3390/POLYM14173511 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14173511
Alam, M. W., Islam Bhat, S., Al Qahtani, H. S., Aamir, M., Amin, M. N., Farhan, M., … Souayeh, B. (2022). Recent Pro-gress, Challenges, and Trends in Polymer-Based Sensors: A Review. Polymers, 14(11), 2164. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14112164 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14112164
Samir, A., Ashour, F. H., Hakim, A. A. A., & Bassyouni, M. (2022). Recent advances in biodegradable polymers for sus-tainable applications. npj Materials Degradation 2022 6:1, 6(1), 1–28. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41529-022-00277-7 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41529-022-00277-7
Hou, W., Xiao, Y., Han, G., & Lin, J. Y. (2019). The Applications of Polymers in Solar Cells: A Review. Polymers 2019, Vol. 11, Page 143, 11(1), 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/POLYM11010143 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11010143
Laftah, W. A., & Wan Abdul Rahman, W. A. (2025). Polymers for anti-fouling applications: a review. Environmental Sci-ence: Advances. https://doi.org/10.1039/D5VA00034C DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/D5VA00034C
Fattah-alhosseini, A., Chaharmahali, R., Alizad, S., Kaseem, M., & Dikici, B. (2024). A review of smart polymeric materi-als: Recent developments and prospects for medicine applications. Hybrid Advances, 5, 100178. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.HYBADV.2024.100178 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hybadv.2024.100178
Bratek-Skicki, A. (2021). Towards a new class of stimuli-responsive polymer-based materials — Recent advances and chal-lenges. Applied Surface Science Advances, 4, 100068. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsadv.2021.100068 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsadv.2021.100068
Lau, W. J., Ismail, A. F., Misdan, N., & Kassim, M. A. (2012). A recent progress in thin film composite membrane: A re-view. Desalination, 287, 190–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.DESAL.2011.04.004 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2011.04.004
Yu, M., Foster, A. B., Kentish, S. E., Scholes, C. A., & Budd, P. M. (2025). Recent progress in thin film composite mem-branes based on the polymer of intrinsic microporosity PIM-1: Preparation, properties and performance. Journal of Membrane Sci-ence, 722, 123844. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MEMSCI.2025.123844 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2025.123844
Wu, L., Song, Y., Xing, S., Li, Y., Xu, H., Yang, Q., & Li, Y. (2022). Advances in electrospun nanofibrous membrane sen-sors for ion detection. RSC Advances, 12(54), 34866–34891. https://doi.org/10.1039/D2RA04911B DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/D2RA04911B
Korolkov, I. V., Narmukhamedova, A. R., Melnikova, G. B., Muslimova, I. B., Yeszhanov, A. B., Zhatkanbayeva, Z. K., … Zdorovets, M. V. (2021). Preparation of Hydrophobic PET Track-Etched Membranes for Separation of Oil–Water Emulsion. Mem-branes 2021, Vol. 11, Page 637, 11(8), 637. https://doi.org/10.3390/MEMBRANES11080637 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11080637
Ma, T., Janot, J. M., & Balme, S. (2020). Track-Etched Nanopore/Membrane: From Fundamental to Applications. Small Methods, 4(9), 2000366. https://doi.org/10.1002/smtd.202000366 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/smtd.202000366
Aimanova, N. A., Almanov, A. A., Alipoori, S., Barsbay, M., Zhumabayev, A. M., Nurpeisova, D. T., Mashentseva, A. A. (2025) Development of the all-solid-state flexible supercapacitor membranes via RAFT-mediated grafting and electrospun nano-fiber modification of track-etched membranes. RSC Advances, 15(8), 6260–6280. https://doi.org/10.1039/d4ra08055f DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/D4RA08055F
Korolkov, I. V., Gorin, Y. G., Yeszhanov, A. B., Kozlovskiy, A. L., & Zdorovets, M. V. (2018). Preparation of PET track-etched membranes for membrane distillation by photo-induced graft polymerization. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 205, 55–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MATCHEMPHYS.2017.11.006 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2017.11.006
Parmanbek, N., Sütekin, D. S., Barsbay, M., Mashentseva, A. A., Zheltov, D. A., Aimanova, N. A., … Zdorovets, M. V. (2022). Hybrid PET Track-Etched Membranes Grafted by Well-Defined Poly(2-(dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate) Brushes and Loaded with Silver Nanoparticles for the Removal of As(III). Polymers, 14(19), 4026. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14194026 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14194026
Barsbay, M., & Güven, O. (2014). Grafting in confined spaces: Functionalization of nanochannels of track-etched mem-branes. Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 105, 26–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RADPHYSCHEM.2014.05.018 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2014.05.018
Shakayeva, A. K., Yeszhanov, A. B., Zhumazhanova, A. T., Korolkov, I. V., & Zdorovets, M. V. (2024). Fabrication of Hy-drophobic PET Track-Etched Membranes using 2,2,3,3,4,4,4-Heptafluorobutyl Methacrylate for Water Desalination by Membrane Distillation. EURASIAN JOURNAL OF CHEMISTRY, 29(2 (114)), 81–88. https://doi.org/10.31489/2959-0663/2-24-5 DOI: https://doi.org/10.31489/2959-0663/2-24-5
Kececi, K. (2023). A Comparable Study of Single Stranded DNA Sensing Using Track-Etched Nanopore Sensors. Chemis-trySelect, 8(37), e202302856. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.202302856 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.202302856
Maity, S., & Tripathi, B. P. (2024). Nanostructured Zwitterionic Membranes: Harnessing Temperature-Responsive Micro-gels for Tunable Water Filtration and Molecular Separation. ACS Applied Polymer Materials, 6(1), 596–606. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsapm.3c02234 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsapm.3c02234
Apel, P. Y. (2025). Intersections of pore channels in track-etched polymer templates and membranes. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 339, 130681. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MATCHEMPHYS.2025.130681 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2025.130681
Apel, P. (2001). Track etching technique in membrane technology. Radiation Measurements, 34(1–6), 559–566. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1350-4487(01)00228-1 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1350-4487(01)00228-1
Zhang, S., Cheng, J., Shi, W., Li, K. -B., Han, D. -M., & Xu, J. -J. (2020). Fabrication of a Biomimetic Nanochannel Logic Platform and Its Applications in the Intelligent Detection of miRNA Related to Liver Cancer. Analytical Chemistry, 92(8), 5952–5959. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.0c00147 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.0c00147
Li, M., Xiong, Y., Lu, W., Wang, X., Liu, Y., Na, B., … Qing, G. (2020). Functional Nanochannels for Sensing Tyrosine Phosphorylation. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 142(38), 16324–16333. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.0c06510 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.0c06510
Li, J., An, P., Qin, C., Sun, C. L., Sun, M., Ji, Z., … Xie, Y. (2020). Bioinspired dual-responsive nanofluidic diodes by poly- l -lysine modification. ACS Omega, 5(9), 4501–4506. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.9b03850
Wang, J., Zhou, Y., & Jiang, L. (2021). Bio-inspired Track-Etched Polymeric Nanochannels: Steady-State Biosensors for Detection of Analytes. ACS Nano, 15(12), 18974–19013. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c08582 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c08582
Armstrong, J. A., Bernal, E. E. L., Yaroshchuk, A., & Bruening, M. L. (2013). Separation of ions using polyelectrolyte-modified nanoporous track-etched membranes. Langmuir, 29(32), 10287–10296. https://doi.org/10.1021/la401934v DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/la401934v
Laucirica, G., Toum Terrones, Y., Cayón, V. M., Cortez, M. L., Toimil-Molares, M. E., Trautmann, C., … Azzaroni, O. (2020). High-sensitivity detection of dopamine by biomimetic nanofluidic diodes derivatized with poly(3-aminobenzylamine). Na-noscale, 12(35), 18390–18399. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0NR03634J
Lalia, B. S., Kochkodan, V., Hashaikeh, R., & Hilal, N. (2013). A review on membrane fabrication: Structure, properties and performance relationship. Desalination, 326, 77–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.DESAL.2013.06.016 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2013.06.016
Esfahani, M. R., Aktij, S. A., Dabaghian, Z., Firouzjaei, M. D., Rahimpour, A., Eke, J., … Koutahzadeh, N. (2019). Nano-composite membranes for water separation and purification: Fabrication, modification, and applications. Separation and Purifica-tion Technology, 213, 465–499. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2018.12.050 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2018.12.050
Zhumanazar, N., Korolkov, I. V., Yeszhanov, A. B., Shlimas, D. I., & Zdorovets, M. V. (2023). Electrochemical detection of lead and cadmium ions in water by sensors based on modified track-etched membranes. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 354, 114094. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SNA.2022.114094 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2022.114094
Mizuguchi, H., Fujiki, S., Shibata, T., Oishi, M., Iiyama, M., Takayanagi, T., … Yeh, M. H. (2023). A flow-based enzyme-free biosensor fabricated using track-etched membrane electrodes: Selective and sensitive detection of uric acid. Sensors and Ac-tuators B: Chemical, 383, 133588. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SNB.2023.133588
Habtamu, H. B., Not, T., De Leo, L., Longo, S., Moretto, L. M., & Ugo, P. (2019). Electrochemical Immunosensor Based on Nanoelectrode Ensembles for the Serological Analysis of IgG-type Tissue Transglutaminase. Sensors, 19(5), 1233. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19051233 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/s19051233
Kozhina, E., Bedin, S., Martynov, A., Andreev, S., Piryazev, A., Grigoriev, Y., … Naumov, A. (2023). Ultrasensitive Opti-cal Fingerprinting of Biorelevant Molecules by Means of SERS-Mapping on Nanostructured Metasurfaces. Biosensors, 13(1), 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/BIOS13010046/S1 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13010046
Zhao, J., Kan, Y., Chen, Z., Li, H., & Zhang, W. (2023). MOFs-Modified Electrochemical Sensors and the Application in the Detection of Opioids. Biosensors 2023, Vol. 13, Page 284, 13(2), 284. https://doi.org/10.3390/BIOS13020284 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13020284
Mashentseva, A. A., Sutekin, D. S., Rakisheva, S. R., & Barsbay, M. (2024). Composite Track-Etched Membranes: Synthe-sis and Multifaced Applications. Polymers, 16(18), 2616. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16182616 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16182616
Li, J., An, P., Qin, C., Sun, C. L., Sun, M., Ji, Z., … Xie, Y. (2020). Bioinspired dual-responsive nanofluidic diodes by poly- l -lysine modification. ACS Omega, 5(9), 4501–4506. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.9b03850 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.9b03850
Soto Espinoza, S., Aguiar, C., Richieri, F., & Grasselli, M. (2019). Track-etched membrane as fluorescence-based pH bio-sensor. Reactive and Functional Polymers, 135, 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2018.11.018 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2018.11.018
Sun, Z., Han, C., Wen, L., Tian, D., Li, H., & Jiang, L. (2012). pH gated glucose responsive biomimetic single nanochan-nels. Chemical Communications, 48(27), 3282. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2cc17277a DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/c2cc17277a
Xu, X., Zhao, W., Gao, P., Li, H., Feng, G., Zhao, Z., & Lou, X. (2016). Coordination of the electrical and optical signals re-vealing nanochannels with an ‘onion-like’ gating mechanism and its sensing application. NPG Asia Materials, 8(1), e234–e234. https://doi.org/10.1038/am.2015.138 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/am.2015.138
Wiedenhöft, L., Elleithy, M. M. A., Ulbricht, M., & Schacher, F. H. (2021). Polyelectrolyte functionalisation of track etched membranes: Towards charge-tuneable adsorber materials. Membranes, 11(7). https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11070509 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11070509
Qian, T., Zhao, C., Wang, R., Chen, X., Hou, J., Wang, H., & Zhang, H. (2021). Synthetic azobenzene-containing metal–organic framework ion channels toward efficient light-gated ion transport at the subnanoscale. Nanoscale, 13(41), 17396–17403. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1NR04595D DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/D1NR04595D
Müller, L. K., Duznovic, I., Tietze, D., Weber, W., Ali, M., Stein, V., … Tietze, A. A. (2020). Ultrasensitive and Selective Copper(II) Detection: Introducing a Bioinspired and Robust Sensor. Chemistry — A European Journal, 26(39), 8511–8517. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.202001160 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.202001160
Shang, Y., Zhang, Y., Li, P., Lai, J., Kong, X. -Y., Liu, W., … Jiang, L. (2015). DNAzyme tunable lead(ii) gating based on ion-track etched conical nanochannels. Chemical Communications, 51(27), 5979–5981. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CC00288E DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CC00288E
Bessbousse, H., Nandhakumar, I., Decker, M., Barsbay, M., Cuscito, O., Lairez, D., … Wade, Travis. L. (2011). Functional-ized nanoporous track-etched β-PVDF membrane electrodes for lead(ii) determination by square wave anodic stripping voltamme-try. Analytical Methods, 3(6), 1351. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1ay05038a DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/c1ay05038a
Barsbay, M., Güven, O., Bessbousse, H., Wade, T. L., Beuneu, F., & Clochard, M. -C. (2013). Nanopore size tuning of pol-ymeric membranes using the RAFT-mediated radical polymerization. Journal of Membrane Science, 445, 135–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2013.05.029 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2013.05.029
Zdorovets, M. V., Korolkov, I. V., Yeszhanov, A. B., & Gorin, Y. G. (2019). Functionalization of PET Track-Etched Mem-branes by UV-Induced Graft (co)Polymerization for Detection of Heavy Metal Ions in Water. Polymers, 11(11), 1876. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11111876 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11111876
Zhumanazar, N. N., Korolkov, I. V., Eszhanov, A. В., Shakayeva, A. Kh., Tashenov, A. К., & Zdorovets, M. V. (2021). Sen-sors Based on Track-Etched Membranes for Electrochemical Detection of Cadmium Ions. NNC RK Bulletin, (1), 4–8. https://doi.org/10.52676/1729-7885-2021-1-5-8 DOI: https://doi.org/10.52676/1729-7885-2021-1-5-8
Omertassov, D. D., Shakayeva, A. Kh., Zhatkanbayeva, Z. K., Shakirzyanov, R. I., Zdorovets, M. V., Güven, O., Korolkov, I. V. (2025). HKUST-1 synthesis in PET Track-Etched membranes via conversion of deposited CU for carbon dioxide capture. ACS Omega, https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.5c01493 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.5c01493
Bessbousse, H., Zran, N., Fauléau, J., Godin, B., Lemée, V., Wade, T., & Clochard, M. -C. (2016). Poly(4-vinyl pyridine) radiografted PVDF track etched membranes as sensors for monitoring trace mercury in water. Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 118, 48–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2015.03.011 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2015.03.011
Korolkov, I. V., Zhumanazar, N., Gorin, Y. G., Yeszhanov, A. B., & Zdorovets, M. V. (2020). Enhancement of electrochem-ical detection of Pb2+ by sensor based on track-etched membranes modified with interpolyelectrolyte complexes. Journal of Mate-rials Science: Materials in Electronics, 31(22), 20368–20377. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-04556-4 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-04556-4
Laucirica, G., Toum Terrones, Y., Cayón, V. M., Cortez, M. L., Toimil-Molares, M. E., Trautmann, C., … Azzaroni, O. (2020). High-sensitivity detection of dopamine by biomimetic nanofluidic diodes derivatized with poly(3-aminobenzylamine). Na-noscale, 12(35), 18390–18399. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0NR03634J DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/D0NR03634J
Ali, M., Nasir, S., & Ensinger, W. (2016). Stereoselective detection of amino acids with protein-modified single asymmetric nanopores. Electrochimica Acta, 215, 231–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2016.08.067 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2016.08.067
Ahlawat, S., Nehra, A., Pandey, V., & Singh, K. P. (2019). Gold-coated nanoporous polycarbonate track–etched solid plat-form for the rapid detection of mesothelin. Ionics, 25(4), 1887–1896. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-018-2761-6 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-018-2761-6
Gaetani, C., Gheno, G., Borroni, M., De Wael, K., Moretto, L. M., & Ugo, P. (2019). Nanoelectrode ensemble immunosens-ing for the electrochemical identification of ovalbumin in works of art. Electrochimica Acta, 312(2019), 72–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2019.04.118 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2019.04.118
Mizuguchi, H., Nishimori, D., Kuwabara, T., Takeuchi, M., Iiyama, M., & Takayanagi, T. (2020). Track-etched membrane-based dual-electrode coulometric detector for microbore/capillary high-performance liquid chromatography. Analytica Chimica Acta, 1102, 46–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2019.12.045 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2019.12.045
Mizuguchi, H., Fujiki, S., Shibata, T., Oishi, M., Iiyama, M., Takayanagi, T., … Yeh, M. H. (2023). A flow-based enzyme-free biosensor fabricated using track-etched membrane electrodes: Selective and sensitive detection of uric acid. Sensors and Ac-tuators B: Chemical, 383(February), 133588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2023.133588 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2023.133588
Bernhard, M., Diefenbach, M., Biesalski, M., & Laube, B. (2020). Electrical Sensing of Phosphonates by Functional Cou-pling of Phosphonate Binding Protein PhnD to Solid-State Nanopores. ACS Sensors, 5(1), 234–241. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.9b02097 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.9b02097
Shakayeva, A. Kh., Munasbaeva, K. K., Zhumazhanova, A. T., Zdorovets, M. V., & Korolkov, I. V. (2023). Electrochemical sensors based on modified track–etched membrane for non-enzymatic glucose determination. Microchemical Journal, 193, 109003. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2023.109003 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2023.109003
Kukushkin, V. I., Kristavchuk, O. V., Zhdanov, G. A., Keshek, A. K., Gambaryan, A. S., Andreev, Y. V., … Zavyalova, E. G. (2023). Aptasensors Based on Track-Etched Membranes Coated with a Nanostructured Silver Layer for Influenza A and B Virus Detection. Bulletin of the Russian Academy of Sciences: Physics, 87(2), 172–177. https://doi.org/10.31857/S0367676522700375 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S1062873822700873
Kukushkin, V., Kristavchuk, O., Andreev, E., Meshcheryakova, N., Zaborova, O., Gambaryan, A., … Zavyalova, E. (2023). Aptamer-coated track-etched membranes with a nanostructured silver layer for single virus detection in biological fluids. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 10, 1076749. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2022.1076749 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2022.1076749
Komatsu, T. (2020). Protein-based smart microtubes and nanotubes as ultrasmall biomaterials. Chemistry Letters, 49(10), 1245–1255. https://doi.org/10.1246/cl.200433 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1246/cl.200433
Komatsu, T., Qu, X., Ihara, H., Fujihara, M., Azuma, H., & Ikeda, H. (2011). Virus Trap in Human Serum Albumin Nano-tube. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 133(10), 3246–3248. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja1096122 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/ja1096122
Karch, H., Tarr, P. I., & Bielaszewska, M. (2005). Enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli in human medicine. International Journal of Medical Microbiology, 295(6–7), 405–418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmm.2005.06.009 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmm.2005.06.009
Yuge, S., Akiyama, M., Ishii, M., Namkoong, H., Yagi, K., Nakai, Y., … Komatsu, T. (2017). Glycoprotein Nanotube Traps Influenza Virus. Chemistry Letters, 46(1), 95–97. https://doi.org/10.1246/cl.160805 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1246/cl.160805
Wang, C., Wu, Z., Liu, B., Zhang, P., Lu, J., Li, J., … Li, C. (2021). Track-etched membrane microplate and smartphone immunosensing for SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 192(August), 113550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2021.113550 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2021.113550
Zhao, Y., Wang, T., Li, Y., Zhao, Z., Xue, J., & Wang, Q. (2024). Fabrication of Breathable Multifunctional On-Skin Elec-tronics Based on Tunable Track-Etched Membranes. ACS Applied Electronic Materials, 6(2), 969–977. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsaelm.3c01414 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsaelm.3c01414
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Semiha D. Sütekin, Saniya R. Rakisheva, Anastassiya A. Mashentseva, Murat Barsbay

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.



