Track-Etched Membranes for Gold Nanowire SERS Substrates
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31489/2959-0663/3-25-11Keywords:
track-etched membrane, template syntesis, gold plating, nanowires, SERS substrate, electrochemical deposition, nanostructures, signal enhancement, intermetallic diffusionAbstract
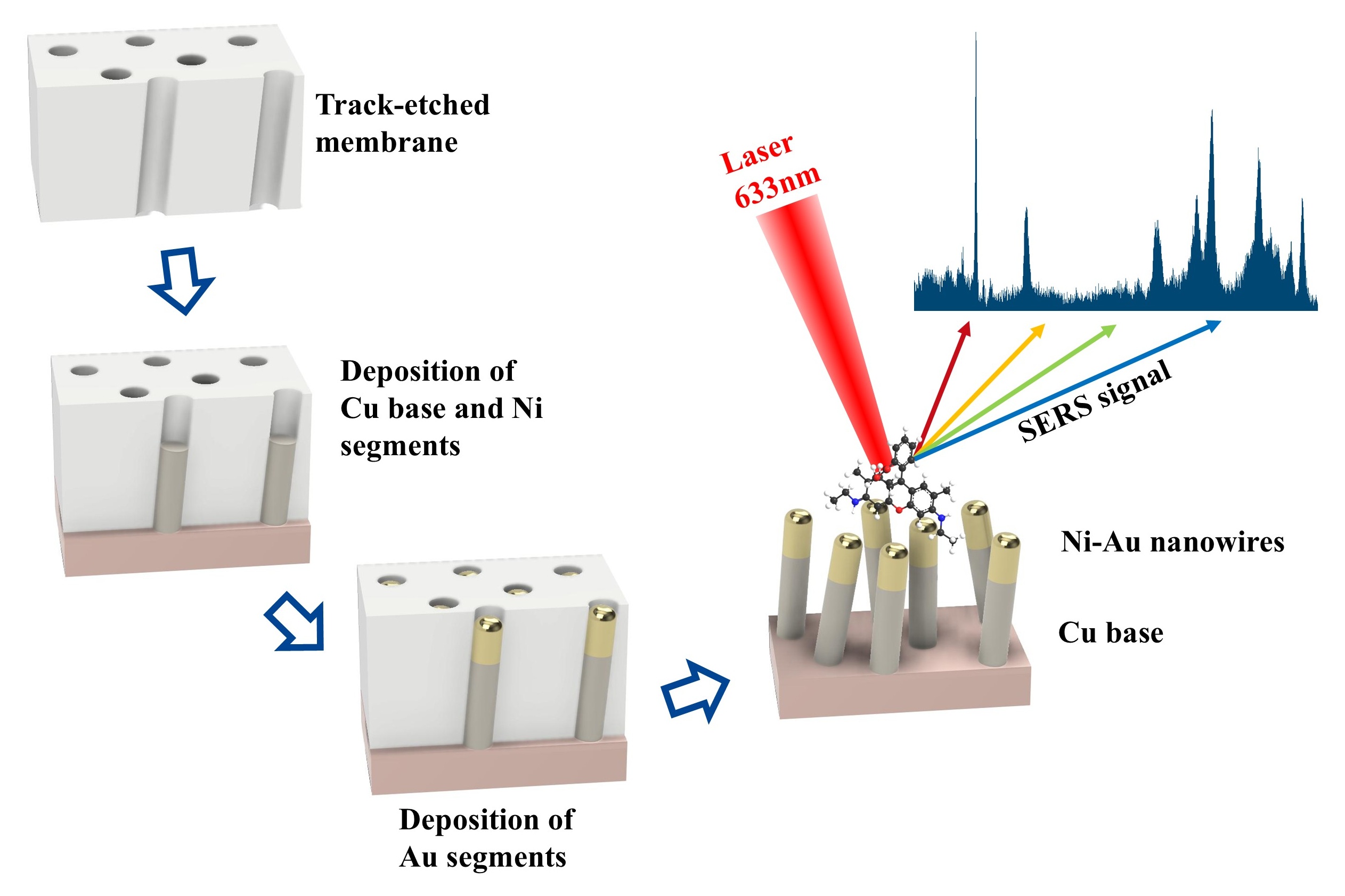
In this study, a novel and reliable method for the production of bimetallic Ni–Au segmented nanowires by template-assisted electrochemical deposition was developed. Track-etched membranes were used as templates for the synthesis of gold nanowires with a diameter of about 100 nm by electrochemical deposition. To enhance structural stability, a modified approach was proposed, wherein gold nanowires were grown on nickel nanowire cores instead of being deposited directly onto the copper layer, as is commonly practiced. The morphology and composition of the resulting nanostructures were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) combined with energy-dispersive X-ray analysis (EDX). Elemental mapping analysis was performed to visualize the spatial distribution of constituent metals within the nanowires, revealing a well-defined segmented architecture: copper was localized at the base, nickel occupied the central region, and gold was selectively deposited on the top surface. The Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) activity of the substrates was evaluated using Rhodamine 6G at the concentration of 10–4 M, confirming their effectiveness for signal enhancement. The developed approach allows precise control of the nanostructures morphology and composition by separating the deposition stages for nickel and gold segments. By eliminating direct contact between gold and copper layers, this strategy effectively suppresses intermetallic diffusion, thereby enhancing the structural stability of the resulting bimetallic nanowires.
References
Wang, L., Wang, X., Cheng, L., Ding, S., Wang, G., Choo, J., & Chen, L. (2021). SERS-based test strips: Principles, designs and applications. Biosens Bioelectron, 189, 113360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2021.113360 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2021.113360
Augustine, S., Saini, M., K.P, S., Parida, B. K., Hans, S., Pachchigar, V., Satpati, B., & Ranjan, M. (2023). Au/Ag SERS ac-tive substrate for broader wavelength excitation. Optical Materials, 135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2022.113319 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2022.113319
Lopez-Lorente, A. I. (2021). Recent developments on gold nanostructures for surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy: Parti-cle shape, substrates and analytical applications. A review. Anal Chim Acta, 1168, 338474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2021.338474 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2021.338474
Martin, C. R. (1994). Nanomaterials: a membrane-based synthetic approach. Science, 266(5193), 1961–1966. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.266.5193.1961 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.266.5193.1961
Kolmychek, I. A., Napolskii, K. S., Leontiev, A. P., Sotnichuk, S. V., & Malysheva, I. V. (2022). Magneto-optical effects in composite hyperbolic metamaterials. Physics of the Solid State, 64(10). https://doi.org/10.21883/pss.2022.10.54226.34hh DOI: https://doi.org/10.21883/PSS.2022.10.54226.34HH
Li, M., Ulrich, N., Schubert, I., Sigle, W., Peter Wagner, M. F., Trautmann, C., & Toimil-Molares, M. E. (2023). Three-dimensional free-standing gold nanowire networks as a platform for catalytic applications. RSC Adv, 13(7), 4721–4728. https://doi.org/10.1039/d2ra08035d DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/D2RA08035D
Apel, P. (2001). Track etching technique in membrane technology. Radiation Measurements, 34(1–6), 559–566. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1350-4487(01)00228-1 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1350-4487(01)00228-1
Oleinikov, V. A., Tolmachyova, Y. V., Berezkin, V. V., Vilensky, A. I., & McHedlishvili, B. V. (1995). Polyethylenetereph-thalate track membranes with conical pores: Etching by water-alcohol alkali solutions. Radiation Measurements, 25(1–4), 713–714. https://doi.org/10.1016/1350-4487(95)00227-6 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/1350-4487(95)00227-6
Cherkasov, D. A., Zagorskii, D. L., Khaibullin, R. I., Muslimov, A. E., & Doludenko, I. M. (2020). Structure and Magnetic Properties of Layered Nanowires of 3d-Metals, Fabricated by the Matrix Synthesis Method. Physics of the Solid State, 62(9), 1695–1705. https://doi.org/10.1134/s1063783420090048 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063783420090048
Kozhina, E., Panov, D., Kovalets, N., Apel, P., & Bedin, S. (2023). A thin-film polymer heating element with a continuous silver nanowires network embedded inside. Nanotechnology, 35(3), 035601. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6528/ad0247 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6528/ad0247
Li, M., Bonart, H., Zellner, D., & Toimil-Molares, M. E. (2025). 3D Gold Nanowire Networks with Tailorable Surface Wet-ting State: From Rose-Petal Effect to Super-Hydrophilicity. Small, 8, Article 2411971. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202411971 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202411971
Kozhina, E. P., Bedin, S. A., Nechaeva, N. L., Podoynitsyn, S. N., Tarakanov, V. P., Andreev, S. N., Grigoriev, Y. V., & Naumov, A. V. (2021). Ag-Nanowire Bundles with Gap Hot Spots Synthesized in Track-Etched Membranes as Effective SERS-Substrates. Applied Sciences, 11(4), 1375. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11041375 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/app11041375
Mashentseva, A. A., Borgekov, D. B., Niyаzova, D. T., & Migunova, A. A. (2015). Study of the structural features of nano-composite materials based on PET track-etched membranes and gold nanotubes. Bulletin of the University of Karaganda-Chemistry, 79(3), 33–40.
Paunovic, M., & Schlesinger, M. (2006). Fundamentals of Electrochemical Deposition. John Wiley & Sons, Inc. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/0470009403
Gruyev, I. D., Matveev, N. I., & Sergeeva, N. G. (1988). Elektrokhimicheskie pokrytiya izdeliy radioelektronnoi apparatury. Spravochnik [Electrochemical Coatings for Radioelectronic Equipment: A Handbook]. Radio i Svyaz. [in Russian]
Cui, S., Su, G., Ren, X., Wu, X., Peng, L., & Fu, Y. (2023). Plasmon Hybridization of Au Hollow Nanocone Array for SERS Sensing. Plasmonics, 19(3), 1395–1402. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-023-02080-9 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-023-02080-9
Liu, J., Duan, J. L., Toimil-Molares, M. E., Karim, S., Cornelius, T. W., Dobrev, D., Yao, H. J., Sun, Y. M., Hou, M. D., Mo, D., Wang, Z. G., & Neumann, R. (2006). Electrochemical fabrication of single-crystalline and polycrystalline Au nanowires: the influence of deposition parameters. Nanotechnology, 17(8), 1922–1926. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/17/8/020 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/17/8/020
Karimian, N., Moretto, L. M., & Ugo, P. (2016). Nanobiosensing with Arrays and Ensembles of Nanoelectrodes. Sensors (Basel), 17(1). https://doi.org/10.3390/s17010065 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/s17010065
Sharma, M. K., Ambolikar, A. S., & Aggarwal, S. K. (2012). Electrochemical synthesis of gold nanorods in track-etched polycarbonate membrane using removable mercury cathode. Journal of Nanoparticle Research, 14(9). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-012-1094-z DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-012-1094-z
Bedin, S., & Kozhina, E. (2024). Ustroĭstvo dlya elektrokhimicheskogo osazhdeniya materiala pri shablonnom sinteze (vari-anty) [Device for electrochemical deposition of material in template synthesis (variants)] (Patent No. RU2820470C1). Federalʹnoe gosudarstvennoe byudzhetnoe uchrezhdenie nauki Fizicheskiĭ institut im. P.N. Lebedeva Rossiĭskoĭ akademii nauk. [in Russian]
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Sergey A. Bedin, Elizaveta P. Kozhina, Ilya M. Doludenko, Vladimir P. Drachev

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.



