Nickel (II) Based Metal-Organic Framework Consolidated on Nanofibers Modified Track-Etched Membrane for Dye Removal
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31489/2959-0663/3-25-7Keywords:
track-etched membranes, metal-organic frameworks, hybrid membranes, nanofibers, electrospinning, dye removal, adsorption, water treatmentAbstract
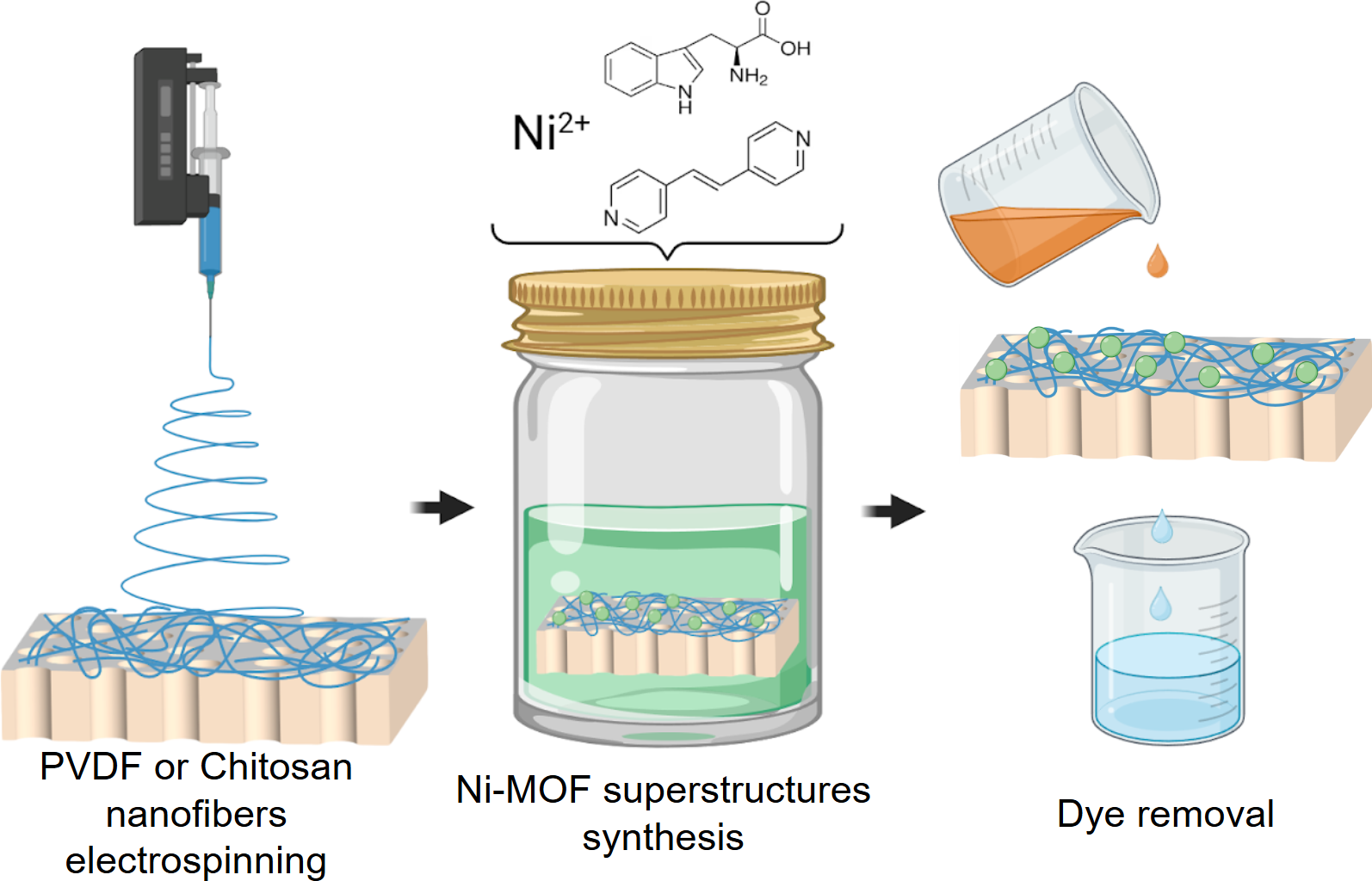
Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) are promising adsorption agents with many potential applications. However, most experiments exploring the potential applications of MOFs have used powders, which limits the range of possible applications. To solve this problem, an approach to design hybrid membrane (HM) based on track-etched membrane, electrospun nanofibers and MOF based on L-tryptophan, 1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethylene and Ni (II) (Ni-MOF) was proposed in the current paper. An investigation of Ni-MOF morphology on hydrophilic chitosan and hydrophobic polyvinylidene fluoride nanofibers showed that the Ni-MOF tends to form superstructures — spherical conglomerates consisting of flaky crystallites on both types of nanofibers. The HMs and Ni-MOF powder were characterized by SEM and PXRD. The adsorption properties of the Ni-MOF powder towards model anionic methyl orange (MO) and cationic rhodamine B (Rh B) including kinetics and isotherm were studied. An investigation of dyes removal by HMs in dead-end filtration mode indicates the effectiveness of MO and Rh B adsorption as high as ~97 % (~380 μg/cm2) and ~9 % (~37 μg/cm2), respectively. The possibility of regeneration was also investigated. Thus, the HMs may find a potential application for advanced wastewater treatment processes to provide removal of MO in microfiltration mode.
References
Farhan Hanafi, M., & Sapawe, N. (2020). A review on the water problem associate with organic pollutants derived from phenol, methyl orange, and remazol brilliant blue dyes. Materials Today: Proceedings, 31, A141–A150. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MATPR.2021.01.258 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.01.258
Habtemariam, T. H., Raju, V. J. T., & Chebude, Y. (2023). Pillared‐Layer Metal‐Organic Frameworks (MOFs) for Photo-degrada-tion of Methyl Orange in Wastewater. Advanced Optical Materials, 11(10). https://doi.org/10.1002/adom.202202843 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/adom.202202843
Kishor, R., Purchase, D., Saratale, G. D., Romanholo Ferreira, L. F., Hussain, C. M., Mulla, S. I., & Bharagava, R. N. (2021). Degradation mechanism and toxicity reduction of methyl orange dye by a newly isolated bacterium Pseudomonas aerugino-sa MZ520730. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 43, 102300. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JWPE.2021.102300 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2021.102300
Ali, I., Burakova, I., Galunin, E., Burakov, A., Mkrtchyan, E., Melezhik, A., Kurnosov, D., Tkachev, A., & Grachev, V. (2019). High-Speed and High-Capacity Removal of Methyl Orange and Malachite Green in Water Using Newly Developed Meso-porous Carbon: Kinetic and Isotherm Studies. ACS Omega, 4(21), 19293–19306. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.9b02669 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.9b02669
Behera, A. K., Shadangi, K. P., & Sarangi, P. K. (2024). Efficient removal of Rhodamine B dye using biochar as an adsor-bent: Study the performance, kinetics, thermodynamics, adsorption isotherms and its reusability. Chemosphere, 354, 141702. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CHEMOSPHERE.2024.141702 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2024.141702
Ghibate, R., Senhaji, O., & Taouil, R. (2021). Kinetic and thermodynamic approaches on Rhodamine B adsorption onto pome-granate peel. Case Studies in Chemical and Environmental Engineering, 3, 100078. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CSCEE.2020.100078 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cscee.2020.100078
Oladoye, P. O., Kadhom, M., Khan, I., Hama Aziz, K. H., & Alli, Y. A. (2024). Advancements in adsorption and photodeg-radation technologies for Rhodamine B dye wastewater treatment: fundamentals, applications, and future directions. Green Chemi-cal Engineering, 5(4), 440–460. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.GCE.2023.12.004 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gce.2023.12.004
Bal, G., & Thakur, A. (2022). Distinct approaches of removal of dyes from wastewater: A review. Materials Today: Pro-ceed-ings, 50, 1575–1579. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MATPR.2021.09.119 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.09.119
Bode-Aluko, C. A., Pereao, O., Ameh, A. E., Omoniyi, E., Nechaev, A., & Petrik, L. (2025). Removal of rhodamine 6G from aqueous solution in a continuous mode using nano-micro composite membranes. Nano Trends, 9, 100096. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.NWNANO.2025.100096 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nwnano.2025.100096
Xiang, W., Wang, Q., Li, Z., Dong, J., Liu, J., Zhang, L., Xia, T., He, Y., & Zhao, D. (2024). Water-stable methyl-modified MOF and mixed matrix membrane for efficient adsorption and separation of cationic dyes. Separation and Purification Technology, 330, 125268. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SEPPUR.2023.125268 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2023.125268
Jiao, L., Seow, J. Y. R., Skinner, W. S., Wang, Z. U., & Jiang, H. L. (2019). Metal–organic frameworks: Structures and func-tional applications. Materials Today, 27, 43–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MATTOD.2018.10.038 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mattod.2018.10.038
Ramírez, D. J., Alfonso Herrera, L. A., Colorado-Peralta, R., Rodríguez, R. P., Camarillo Reyes, P. K., Chiñas, L. E., Sánchez, M., & Rivera, J. M. (2021). Highly efficient methyl orange adsorption by UV-012, a new crystalline Co(II) MOF. CrystEngComm, 23(19), 3537–3548. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CE00741B DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CE00741B
Sağlam, S., Türk, F. N., & Arslanoğlu, H. (2023). Use and applications of metal-organic frameworks (MOF) in dye adsorp-tion: Review. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 11(5), 110568. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JECE.2023.110568 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2023.110568
Huang, J., Huang, D., Zeng, F., Ma, L., & Wang, Z. (2021). Photocatalytic MOF fibrous membranes for cyclic adsorption and degradation of dyes. Journal of Materials Science, 56(4), 3127–3139. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-05473-x DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-05473-x
Markov, P. A., Vinogradov, I. I., Kostromina, E., Eremin, P. S., Gilmutdinova, I. R., Kudryashova, I. S., Greben, A., Rachin, A. P., & Nechaev, A. N. (2022). A wound dressing based on a track-etched membrane modified by a biopolymer nanoframe: physi-cochemical and biological characteristics. European Polymer Journal, 181, 111709. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.EURPOLYMJ. 2022.111709 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2022.111709
Pereao, O., Uche, C., Bublikov, P. S., Bode-Aluko, C., Rossouw, A., Vinogradov, I. I., Nechaev, A. N., Opeolu, B., & Petrik, L. (2021). Chitosan/PEO nanofibers electrospun on metallized track-etched membranes: fabrication and characterization. Materials Today Chemistry, 20, 100416. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MTCHEM.2020.100416 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtchem.2020.100416
Vinogradov, I. I., Petrik, L., Serpionov, G. V., & Nechaev, A. N. (2021). Composite Membrane Based on Track-Etched Mem-brane and Chitosan Nanoscaffold. Membranes and Membrane Technologies, 3(6), 400–410. https://doi.org/10.1134/S2517751621060093 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S2517751621060093
Vinogradov, I. I., Andreev, E. V., Yushin, N. S., Sokhatskii, A. S., Altynov, V. A., Gustova, M. V., Vershinina, T. N., Zin’kovskaya, I., Nechaev, A. N., & Apel’, P. Yu. (2023). A Hybrid Membrane for the Simultaneous Selective Sorption of Cesium in the Ionic and Colloid Forms. Theoretical Foundations of Chemical Engineering, 57(4), 549–562. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0040579523040498 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0040579523040498
Vinogradov, I. I., Drozhzhin, N. A., Kravets, L. I., Rossouw, A., Vershinina, T. N., & Nechaev, A. N. (2024). Formation of Hybrid Membranes for Water Desalination by Membrane Distillation. Colloid Journal, 86(5), 667–679. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1061933X24600519 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1061933X24600519
Rossouw, A., Olejniczak, A., Olejniczak, K., Gorberg, B., Vinogradov, I., Kristavchuk, O., Nechaev, A., Petrik, L., Perold, W., & Dmitriev, S. (2022). Ti and TiO2 magnetron sputtering in roll-to-roll fabrication of hybrid membranes. Surfaces and Inter-faces, 31, 101975. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SURFIN.2022.101975 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2022.101975
Ivanshina, O. Yu., Zuba, I., Sumnikov, S. V., Nabiyev, A. A., & Pawlukojć, A. (2021). L-Tryptophan metal-organic frame-works based on transition metals: Preparation, characterization and application for ruthenium 3+ ions sorption. 020001. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0063607 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0063607
Ponomareva, O. Yu., Drozhzhin, N. A., Vinogradov, I. I., Vershinina, T. N., Altynov, V. A., Zuba, I., Nechaev, A. N., & Pawlukojć, A. (2024). Metal–Organic Framework Based on Nickel, L-Tryptophan, and 1,2-Bis(4-Pyridyl)Ethylene, Consolidat-ed on a Track-Etched Membrane. Russian Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 69(6), 914–924. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0036023624600667 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0036023624600667
Ho, Y. S. (2006). Review of second-order models for adsorption systems. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 136(3), 681–689. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2005.12.043 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.12.043
Lu, H., Yang, Q., Huang, B., Qi, J., Wang, R., Zhou, Q., Chen, Q., Zhu, L., Jin, J., & Kong, Y. (2023). Removal performance and adsorption kinetics of dyes by a Co-based metal organic framework. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 360, 112665. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MICROMESO.2023.112665 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2023.112665
Abin-Bazaine, A., Campos Trujillo, A., & Olmos-Marquez, M. (2022). Adsorption Isotherms: Enlightenment of the Phe-nomenon of Adsorption. In Wastewater Treatment. IntechOpen. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.104260 DOI: https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.104260
Sahoo, T. R., & Prelot, B. (2020). Adsorption processes for the removal of contaminants from wastewater: the perspective role of nanomaterials and nanotechnology. Nanomaterials for the Detection and Removal of Wastewater Pollutants, 161–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-818489-9.00007-4 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-818489-9.00007-4
Li, X., Wang, J., Zhang, X., & Chen, C. (2015). Powdered activated carbon adsorption of two fishy odorants in water: Trans, trans-2,4-heptadienal and trans, trans-2,4-decadienal. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 32, 15–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JES.2015.01.001 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2015.01.001
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Nikita A. Drozhzhin, Olga Yu. Ponomareva, Ilya I. Vinogradov, Genrikh V. Serpionov, Abubakir Kanet, Daria V. Nikolskaya, Tatiana N. Vershinina

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.



