Radiation Grafting of PVDF Track-Etched Membranes: A Study for Nanoscale Pore Functionalization
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31489/2959-0663/3-25-9Keywords:
swift heavy ions, track-etched membrane, polyvinylidene fluoride, radiation grafting, acrylic acid, nanoporous membranes, pore functionalization, ion-irradiatedAbstract
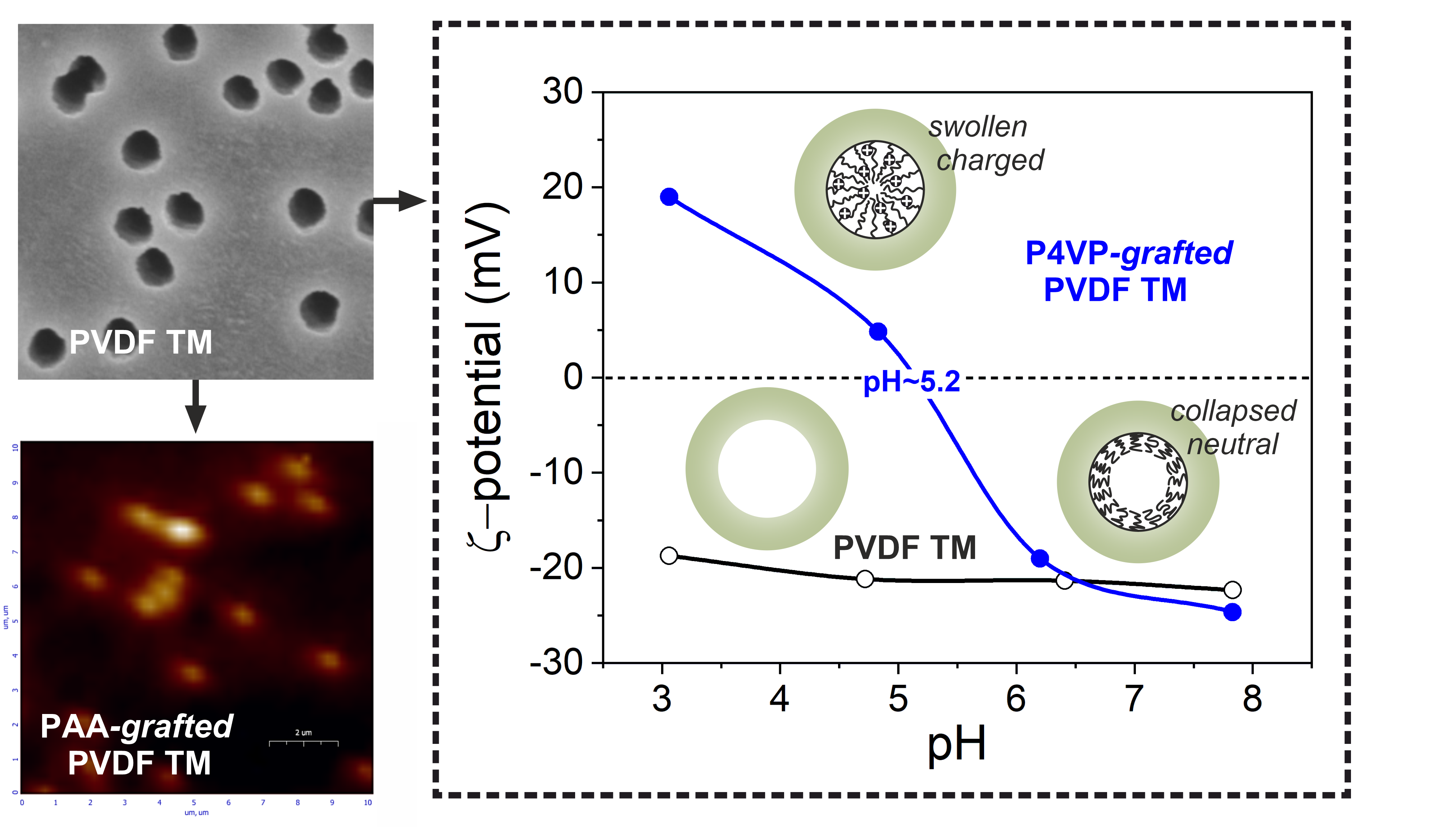
Functionalization of nanoporous membranes poses a substantial challenge in the development of advanced materials for selective transport applications. The primary objective of this study is to optimize the grafting process to ensure the functionalization is localized onto nanopore walls. Poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) foils were irradiated with Xe ions (1.2 MeV/u) followed by subsequent etching under optimized conditions to create nanoporous membranes. Radiation grafting of acrylic acid (AA) monomer was performed through the residual radical sites in post-etched pore walls of ion-irradiated PVDF. Radical concentrations after irradiation were quantified using EPR spectroscopy. Examination of reaction parameters including inhibitor concentration, temperature, monomer concentration, and reaction kinetics was conducted to achieve selective grafting within the nanopores. FT-IR and XPS analyses confirmed the successful covalent attachment of poly(acrylic acid) (PAA) to the PVDF TMs. Structural transformations of the PVDF matrix throughout the functionalization process were revealed by DSC analysis. The versatility of the approach was further demonstrated by grafting of pH-responsive poly(4-vinylpyridine), enabling modulation of nanopore surface charge, as evidenced by zeta-potential measurements. The spatial localization of the grafted polymer was confirmed by confocal fluorescence microscopy, demonstrating the potential for creating advanced functional membranes for separation and sensing applications.
References
Nasef, M. M., & Güven, O. (2012). Radiation-grafted copolymers for separation and purification purposes: Status, challenges and future directions. Progress in Polymer Science, 37(12), 1597–1656. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2012.07.004 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2012.07.004
Saxena, P., & Shukla, P. (2021). A comprehensive review on fundamental properties and applications of poly (vinylidene fluoride)(PVDF). Advanced Composites and Hybrid Materials, 4(1), 8–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-021-00217-0 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-021-00217-0
Costa, C. M., Cardoso, V. F., Pedro, M., Correia, D. M., Gonçalves, R., Costa, P., Correia, V., Ribeiro, C., Fernandes, M. M., Martins, P. M., & Lanceros-Méndez, S. (2023). Smart and multifunctional materials based on electroactive poly (vinylidene fluoride): recent advances and opportunities in sensors, actuators, energy, environmental, and biomedical applications. Chemical reviews, 123(19), 11392–11487. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.3c00196 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.3c00196
Apel, P. Y. (2019). Fabrication of functional micro-and nanoporous materials from polymers modified by swift heavy ions. Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 159, 25–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2019.01.0 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2019.01.009
Ma, T., Janot, J. M., Balme, S.(2020). Track‐etched nanopore/membrane: from fundamental to applications. Small Methods, 4(9), 2000366. https://doi.org/10.1002/smtd.202000366 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/smtd.202000366
Barsbay, M., & Güven, O. (2014). Grafting in confined spaces: Functionalization of nanochannels of track-etched membranes. Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 105, 26–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2014.05.018 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2014.05.018
Chapiro, A. (1959). Préparation des copolymères greffés du polytetrafluoroéthylène (Teflon) par voie radiochimique. Journal of Polymer Science, 34(127), 481–501. https://doi.org/10.1002/pol.1959.1203412735 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/pol.1959.1203412735
Dargaville, T. R., George, G. A., Hill, D. J. T., & Whittaker, A. K. (2003). High energy radiation grafting of fluoropolymers. Progress in Polymer Science, 28(9), 1355–1376. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0079-6700(03)00047-9 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0079-6700(03)00047-9
Chapiro, A. (1977). Radiation induced grafting. Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 9(1-3), 55–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/0146-5724(77)90072-3 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0146-5724(77)90072-3
Ellinghorst, G., Niemöller, A., & Vierkotten, D. (1983). Radiation initiated grafting of polymer films — an alternative technique to prepare membranes for various separation problems. Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 22(3-5), 635–642. https://doi.org/10.1016/0146-5724(83)90073-0 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0146-5724(83)90073-0
Betz, N. (1995). Ion track grafting. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms, 105(1-4), 55–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/0168-583x(95)00911-6 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0168-583X(95)00911-6
Clochard, M.-C., Bégué, J.-P., Lafon, A., Caldemaison, D., Bittencourt, C., Pireaux, J. J., & Betz, N. (2004). Tailoring bulk and surface grafting of poly(acrylic acid) in electron-irradiated PVDF. Polymer, 45(26), 8683–8694. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2004.10.052 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2004.10.052
Mazzei, R., Bermúdez, G. G., Betz, N., & Cabanillas, E. (2004). Swift heavy ion induced graft polymerization in track etched membranes’ submicroscopic pores. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms, 226(4), 575–584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nimb.2004.08.001 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nimb.2004.08.001
Mazzei, R., García Bermúdez, G., Camporotondi, D. E., Arbeitman, C., del Grosso, M. F., & Behar, M. (2012). New membranes obtained by grafted irradiated PVDF foils. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms, 287, 26–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nimb.2012.05.040 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nimb.2012.05.040
Mazzei, R., Betz, N., Bermúdez, G. G., Massa, G., & Smolko, E. (2005). Submicroscopic pores grafted using the residual sites produced by swift heavy ions. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms, 236(1-4), 407–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nimb.2005.04.007 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nimb.2005.04.007
Cuscito, O., Clochard, M. -C., Esnouf, S., Betz, N., & Lairez, D. (2007). Nanoporous β-PVDF membranes with selectively functionalized pores. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms, 265(1), 309–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nimb.2007.08.089 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nimb.2007.08.089
Barsbay, M., Güven, O., Bessbousse, H., Wade, T., Beuneu, F., & Clochard, M. -C. (2013). Nanopore size tuning of polymeric membranes using the RAFT-mediated radical polymerization. Journal of Membrane Science, 445, 135–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2013.05.029 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2013.05.029
Tretyakova, S. P., Shirkova, V. V., Khitrova, N. B., & Borcea, C. (1986). Polyvinylidenfluoride (PVF) as a charged particle detector. Nucl. Tracks Radiat. Meas., 12. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/1359-0189(86)90541-8
Balanzat, E., Bouffard, S., A. Le Moël, & Betz, N. (1994). Physico-chemical modifications induced in polymers by swift heavy ions. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms, 91(1-4), 140–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/0168-583x(94)96204-9 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0168-583X(94)96204-9
Bogar, M. S., Beuermann, S., Dmitrieva, E., Drache, M., Gohs, U., Kunz, U., Lemmermann, T., Rosenkranz, M., Stehle, M., & Zschech, C. (2021). Quantitative EPR study of poly(vinylidene fluoride) activated by electron beam treatment. Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 184, 109421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2021.109421 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2021.109421
Komaki, Y., Ishikawa, N., Morishita, N., & Takamura, S. (1996). Radicals in heavy ion-irradiated polyvinylidene fluoride. Radiation Measurements, 26(1), 123–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/1350-4487(95)00286-3 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/1350-4487(95)00286-3
Betz, N., Petersohn, E., & Le Moël, A. (1996). Free radicals in swift heavy ion irradiated fluoropolymers: An electron spin resonance study. Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 47(3), 411–414. https://doi.org/10.1016/0969-806x(95)00127-j DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0969-806X(95)00127-J
Goslar, J., Hilczer, & B., Smogór, H. (2005). ESR studies of fast electron irradiated ferroelectric poly (vinylidene fluoride). Acta Physica Polonica A, 108(1), 89–94. DOI: https://doi.org/10.12693/APhysPolA.108.89
Tretyakova, S. P., & Jolos, L. V. (1978). Heavy ion particle track detector of fluoropolymers. Prib. Tekh. Eksp., 1, 36–41.
Grasselli, M., & Betz, N. (2005). Making porous membranes by chemical etching of heavy-ion tracks in β-PVDF films. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms, 236(1-4), 501–507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nimb.2005.04.027 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nimb.2005.04.027
Pinaeva, U., Dietz, T. C., Sheikhly, M. -Al., Balanzat, E., Castellino, M., Wade, T. L., & Clochard, M. -C. (2019). Bis[2-(methacryloyloxy)ethyl] phosphate radiografted into track-etched PVDF for uranium (VI) determination by means of cathodic stripping voltammetry. Reactive and Functional Polymers, 142, 77–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2019.06.006 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2019.06.006
Betz, N., Begue, J., Goncalves, M., K. Gionnet, G. Déléris, & A. Le Moël. (2003). Functionalisation of PAA radiation grafted PVDF. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms, 208, 434–441. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0168-583x(03)00900-5 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-583X(03)00900-5
Zhou, Z., Li, W., He, T., Qian, L., Tan, G., & Ning, C. (2016). Polarization of an electroactive functional film on titanium for inducing osteogenic differentiation. Scientific Reports, 6(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep35512 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/srep35512
Volgina, E., Pinaeva, U., Temnov, D., Ivanov, O., Mitrofanov, S., & Nechaev, A. (2025). Relaxation processes in swift heavy ion irradiated poly(vinylidene fluoride) films. Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 230, 112593. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2025.112593 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2025.112593
Betz, N., Petersohn, E., & Le Moël, A. (1996). Swift heavy ions effects in fluoropolymers: radicals and crosslinking. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms, 116(1-4), 207–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/0168-583x(96)00125-5 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0168-583X(96)00125-5
Percolla, R., Musumeci, P., Calcagno, L., Foti, G., & Ciavola, G. (1995). Grafting of styrene in polyvinylidene fluoride by high energy ion irradiation. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms, 105(1-4), 181–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/0168-583x(95)00636-2 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0168-583X(95)00636-2
Wang, H., Lee, I. H., & Yan, M. (2012). A general method to determine ionization constants of responsive polymer thin films. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 365(1), 178–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2011.08.081 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2011.08.081
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Angelina V. Seliverstrova-Krukova, Oleg L. Orelovich , Vladimir A. Altynov, Alexander V. Akimov, Alexander S. Shmakov, Daria V. Nikolskaya, Nikita S. Kirilkin, Uliana V. Pinaeva

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.



