Synthesis and Optimization of Bovine Serum Albumin Nanoparticles Immobilized with Antituberculosis Drugs
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31489/2959-0663/1-24-6Keywords:
nanoparticles, bovine serum albumin, rifampicin, isoniazid, desolvation, hydrophilic drugs, hydrophobic drugs, anti-tuberculosis drugsAbstract
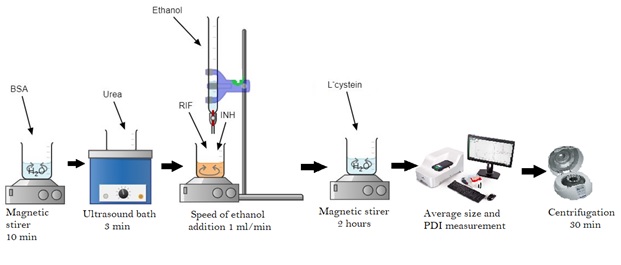
This study involved the synthesis of bovine serum albumin (BSA) nanoparticles immobilized with the antituberculosis drugs isoniazid (INH) and rifampicin (RIF) by the desolvation method. The primary objective was to explore the impact of varying concentrations of albumin, urea, cysteine, rifampicin, and isoniazid on the average size of nanoparticles, polydispersity, and the encapsulation efficiency of drugs. The study's outcomes affirm that alterations in the concentrations of these components influence nanoparticles’ parameters, highlighting their key role in optimizing the encapsulation process and enhancing the efficacy of tuberculosis drug delivery. The nanoparticles obtaned as a result of optimization demonstrated an optimal size of 231.2±1.2 nm with a polydispersity of 0.061±0.08. Encapsulation efficiency was 89% for rifampicin and 38.5% for isoniazid. The investigation of drug release kinetics from the polymer matrix revealed a gradual release pattern. Evaluation of the obtained nanoparticles by Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) confirmed the successful incorporation of drugs into the polymer matrix. These findings highlight the potential of BSA nanoparticles as effective carriers for tuberculosis treatment, with implications for refining drug delivery strategies.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.



