Synthesis, Characterization and Application of New Polymers Imprinted with Zinc (II) Ions
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31489/2959-0663/2-24-14Keywords:
molecular imprinted polymers, comparison polymer, sodium humate, polyvinyl alcohol, template, zinc, sorption, adsorbentAbstract
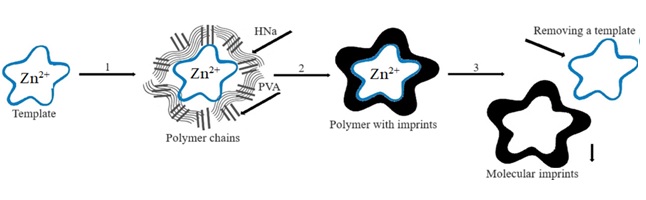
In this work, molecularly imprinted polymers with zinc imprints and their comparison polymers without imprints were synthesized. A comparative characterization of the physical parameters of the synthesized zinc-imprinted (ZnIP) and non-imprinted (NIP) polymers was carried out using the methods of elemental analysis, conductometry, scanning electron microscopy, and IR-Fourier spectroscopy. The ability of the resulting polymers to molecularly recognize zinc was evaluated. Based on experimental data on static adsorption, the adsorption capacity of ZnIP and NIP was determined using an atomic emission spectrometer. It was found that ZnIP is characterized by better physical parameters and a higher ability for molecular recognition of zinc compared to NIP. ZnIP with zinc imprints were found to have better sorption capacity for zinc than their reference polymers. The sorption of zinc by molecular imprinted ZnIP is mainly due to the complex formation and pores of the initial carbon product. The synthesized ZnIP have increased porosity. The presence of pores with a diameter <50 nm in ZnIP is associated with voids formed after acid hydrolysis, which is clearly visible in images recorded by scanning electron microscopy. Thus, the possibility of using ZnIP as a selective sorbent has been established.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Yevgeniy Vassilets, Alma Zhakina, Oxana Arnt, Arailym Alzhankyzy, Almat Zhakin

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.



